Page 27 - Banking Finance June 2025
P. 27
ARTICLE
What are cross border payments? How do Cross Border Payments work
Cross border payments basically refer to transactions where In international money transfers physical currency is not
the payer and the payee are located in different countries. transferred overseas. Neither can transactions in foreign
These payments may be in form of cross border remittances, currency be made through domestic payments system. So,
international trade transactions like exports and imports, to overcome this peculiar problem, international banks do
eCommerce payments or investment transfers. what is called Correspondent Banking. Under this model,
they maintain accounts of foreign banks with them and vice
Table 1: Cross Border Transaction types versa. These accounts are known as the Nostro-Vostro ac-
counts. The funds are credited in the Nostro account in one
Transaction Examples of Cross
country and corresponding amount is debited in the Nostro
types Border Payments
account in another jurisdiction. Let us understand the pro-
Business-to-Business (B2B) International trade cess by way of an example:
transactions transactions like exports
and imports
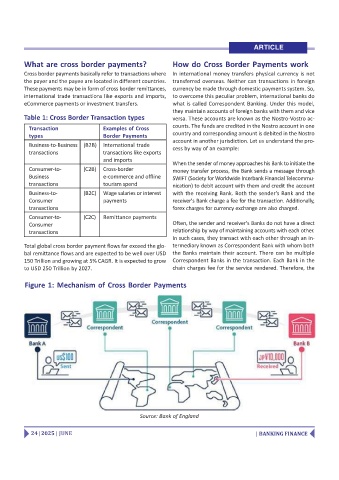
When the sender of money approaches his Bank to initiate the
Consumer-to- (C2B) Cross-border money transfer process, the Bank sends a message through
Business e-commerce and offline SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommu-
transactions tourism spend nication) to debit account with them and credit the account
Business-to- (B2C) Wage salaries or interest with the receiving Bank. Both the sender's Bank and the
Consumer payments receiver's Bank charge a fee for the transaction. Additionally,
transactions forex charges for currency exchange are also charged.
Consumer-to- (C2C) Remittance payments
Consumer Often, the sender and receiver's Banks do not have a direct
transactions relationship by way of maintaining accounts with each other.
In such cases, they transact with each other through an in-
Total global cross border payment flows far exceed the glo- termediary known as Correspondent Bank with whom both
bal remittance flows and are expected to be well over USD the Banks maintain their account. There can be multiple
150 Trillion and growing at 5% CAGR. It is expected to grow Correspondent Banks in the transaction. Each Bank in the
to USD 250 Trillion by 2027. chain charges fee for the service rendered. Therefore, the
Figure 1: Mechanism of Cross Border Payments
Source: Bank of England
24 | 2025 | JUNE | BANKING FINANCE