Page 180 - Operations Strategy
P. 180
WHAT is PuRCHAsing And suPPly sTRATEgy? 155
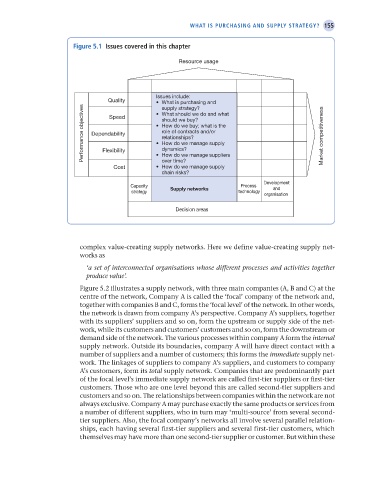
Figure 5.1 issues covered in this chapter
Resource usage
Issues include:
Quality What is purchasing and
Performance objectives Dependability should we buy? Market competitiveness
supply strategy?
What should we do and what
Speed
How do we buy; what is the
role of contracts and/or
relationships?
How do we manage supply
dynamics?
Flexibility
over time?
Cost How do we manage suppliers
How do we manage supply
chain risks?
Development
Capacity Supply networks Process and
strategy technology
organisation
Decision areas
complex value-creating supply networks. Here we define value-creating supply net-
works as
‘a set of interconnected organisations whose different processes and activities together
produce value’.
Figure 5.2 illustrates a supply network, with three main companies (A, B and C) at the
centre of the network, Company A is called the ‘focal’ company of the network and,
together with companies B and C, forms the ‘focal level’ of the network. In other words,
the network is drawn from company A’s perspective. Company A’s suppliers, together
with its suppliers’ suppliers and so on, form the upstream or supply side of the net-
work, while its customers and customers’ customers and so on, form the downstream or
demand side of the network. The various processes within company A form the internal
supply network. Outside its boundaries, company A will have direct contact with a
number of suppliers and a number of customers; this forms the immediate supply net-
work. The linkages of suppliers to company A’s suppliers, and customers to company
A’s customers, form its total supply network. Companies that are predominantly part
of the focal level’s immediate supply network are called first-tier suppliers or first-tier
customers. Those who are one level beyond this are called second-tier suppliers and
customers and so on. The relationships between companies within the network are not
always exclusive. Company A may purchase exactly the same products or services from
a number of different suppliers, who in turn may ‘multi-source’ from several second-
tier suppliers. Also, the focal company’s networks all involve several parallel relation-
ships, each having several first-tier suppliers and several first-tier customers, which
themselves may have more than one second-tier supplier or customer. But within these
M05 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 155 02/03/2017 13:04