Page 93 - Operations Strategy
P. 93
68 CHAPTER 2 • OPERATiOns PERfORmAnCE
the relative importance of performance objectives
changes over time
In addition to the ‘erosion’ effect mentioned previously, there are more generic changes
caused by the way markets change over time and operations resource capabilities
develop over time. Not surprising, then, that the nature of the reconciliation process,
and therefore the role of operations strategy, changes over time – though the stimulus
for change may vary. At some times markets change fast: competitors may be particu-
larly aggressive, or novel products or services may redefine customer expectations. If so,
the competitive agenda for the business will be influenced largely by how the organisa-
tion positions itself in its markets.
Changes in the firm’s markets – the product/service life cycle influence
on performance
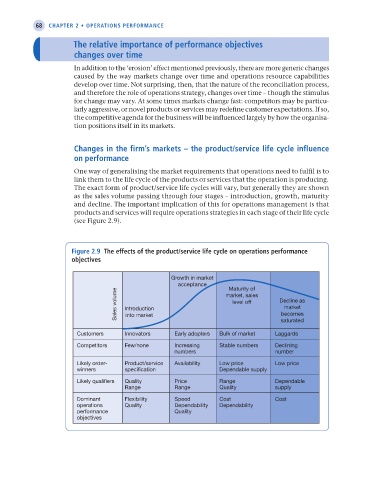
One way of generalising the market requirements that operations need to fulfil is to
link them to the life cycle of the products or services that the operation is producing.
The exact form of product/service life cycles will vary, but generally they are shown
as the sales volume passing through four stages – introduction, growth, maturity
and decline. The important implication of this for operations management is that
products and services will require operations strategies in each stage of their life cycle
(see Figure 2.9).
Figure 2.9 The effects of the product/service life cycle on operations performance
objectives
Growth in market
acceptance Maturity of
Sales volume Introduction market, sales Decline as
level o
market
becomes
into market
saturated
Customers Innovators Early adopters Bulk of market Laggards
Competitors Few/none Increasing Stable numbers Declining
numbers number
Likely order- Product/service Availability Low price Low price
winners specification Dependable supply
Likely qualifiers Quality Price Range Dependable
Range Range Quality supply
Dominant Flexibility Speed Cost Cost
operations Quality Dependability Dependability
performance Quality
objectives
M02 Operations Strategy 62492.indd 68 02/03/2017 13:01