Page 31 - Libro 2
P. 31
1 — Vascular Anatomy
11
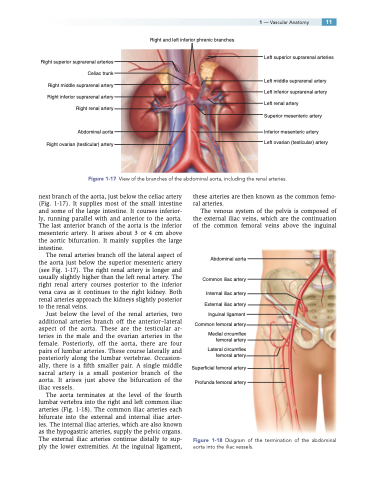
Right and left inferior phrenic branches
Right superior suprarenal arteries Celiac trunk Right middle suprarenal artery Right inferior suprarenal artery Right renal artery
Abdominal aorta Right ovarian (testicular) artery
Left superior suprarenal arteries
Left middle suprarenal artery Left inferior suprarenal artery Left renal artery
Superior mesenteric artery
Inferior mesenteric artery Left ovarian (testicular) artery
Figure 1-17 View of the branches of the abdominal aorta, including the renal arteries.
next branch of the aorta, just below the celiac artery (Fig. 1-17). It supplies most of the small intestine and some of the large intestine. It courses inferior- ly, running parallel with and anterior to the aorta. The last anterior branch of the aorta is the inferior mesenteric artery. It arises about 3 or 4 cm above the aortic bifurcation. It mainly supplies the large intestine.
The renal arteries branch off the lateral aspect of the aorta just below the superior mesenteric artery (see Fig. 1-17). The right renal artery is longer and usually slightly higher than the left renal artery. The right renal artery courses posterior to the inferior vena cava as it continues to the right kidney. Both renal arteries approach the kidneys slightly posterior to the renal veins.
Just below the level of the renal arteries, two additional arteries branch off the anterior–lateral aspect of the aorta. These are the testicular ar- teries in the male and the ovarian arteries in the female. Posteriorly, off the aorta, there are four pairs of lumbar arteries. These course laterally and posteriorly along the lumbar vertebrae. Occasion- ally, there is a fifth smaller pair. A single middle sacral artery is a small posterior branch of the aorta. It arises just above the bifurcation of the iliac vessels.
The aorta terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra into the right and left common iliac arteries (Fig. 1-18). The common iliac arteries each bifurcate into the external and internal iliac arter- ies. The internal iliac arteries, which are also known as the hypogastric arteries, supply the pelvic organs. The external iliac arteries continue distally to sup- ply the lower extremities. At the inguinal ligament,
these arteries are then known as the common femo- ral arteries.
The venous system of the pelvis is composed of the external iliac veins, which are the continuation of the common femoral veins above the inguinal
Abdominal aorta
Common iliac artery
Internal iliac artery
External iliac artery Inguinal ligament Common femoral artery
Medial circumflex femoral artery
Lateral circumflex femoral artery
Superficial femoral artery Profunda femoral artery
Figure 1-18 Diagram of the termination of the abdominal aorta into the iliac vessels.