Page 102 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 102
Intestinal Nematodes: Non-Soil Transmitted Helminths 95
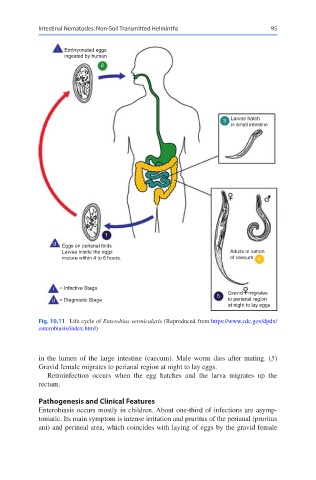
i Embryonated eggs
ingested by human
2
3 Larvae hatch
in small intestine
1
d Eggs on perianal folds
Larvae inside the eggs Adults in lumen
mature within 4 to 6 hours. of caecum 4
i = Infective Stage
5 Gravid migrates
d = Diagnostic Stage to perianal region
at night to lay eggs
Fig. 10.11 Life cycle of Enterobius vermicularis (Reproduced from https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/
enterobiasis/index.html)
in the lumen of the large intestine (caecum). Male worm dies after mating. (5)
Gravid female migrates to perianal region at night to lay eggs.
Retroinfection occurs when the egg hatches and the larva migrates up the
rectum.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Features
Enterobiasis occurs mostly in children. About one-third of infections are asymp-
tomatic. Its main symptom is intense irritation and pruritus of the perianal (pruritus
ani) and perineal area, which coincides with laying of eggs by the gravid female