Page 161 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 161
154 13 Ectoparasites of Medical Importance
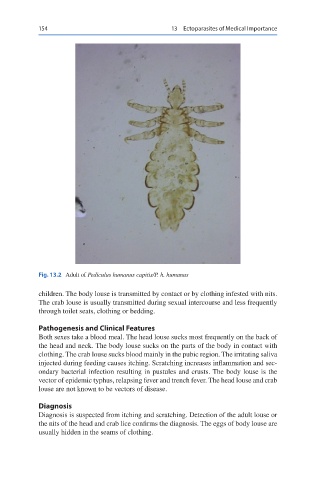
Fig. 13.2 Adult of Pediculus humanus capitis/P. h. humanus
children. The body louse is transmitted by contact or by clothing infested with nits.
The crab louse is usually transmitted during sexual intercourse and less frequently
through toilet seats, clothing or bedding.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Features
Both sexes take a blood meal. The head louse sucks most frequently on the back of
the head and neck. The body louse sucks on the parts of the body in contact with
clothing. The crab louse sucks blood mainly in the pubic region. The irritating saliva
injected during feeding causes itching. Scratching increases inflammation and sec-
ondary bacterial infection resulting in pustules and crusts. The body louse is the
vector of epidemic typhus, relapsing fever and trench fever. The head louse and crab
louse are not known to be vectors of disease.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is suspected from itching and scratching. Detection of the adult louse or
the nits of the head and crab lice confirms the diagnosis. The eggs of body louse are
usually hidden in the seams of clothing.