Page 61 - Medical Parasitology_ A Textbook ( PDFDrive )
P. 61
54 7 Coccidia
a b
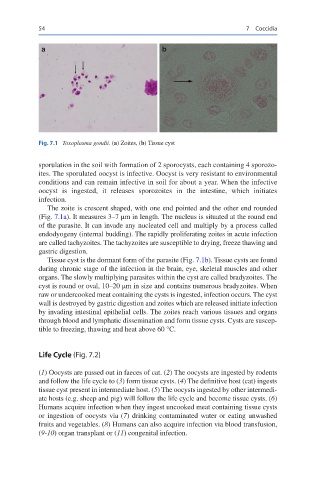
Fig. 7.1 Toxoplasma gondii. (a) Zoites, (b) Tissue cyst
sporulation in the soil with formation of 2 sporocysts, each containing 4 sporozo-
ites. The sporulated oocyst is infective. Oocyst is very resistant to environmental
conditions and can remain infective in soil for about a year. When the infective
oocyst is ingested, it releases sporozoites in the intestine, which initiates
infection.
The zoite is crescent shaped, with one end pointed and the other end rounded
(Fig. 7.1a). It measures 3–7 μm in length. The nucleus is situated at the round end
of the parasite. It can invade any nucleated cell and multiply by a process called
endodyogeny (internal budding). The rapidly proliferating zoites in acute infection
are called tachyzoites. The tachyzoites are susceptible to drying, freeze thawing and
gastric digestion.
Tissue cyst is the dormant form of the parasite (Fig. 7.1b). Tissue cysts are found
during chronic stage of the infection in the brain, eye, skeletal muscles and other
organs. The slowly multiplying parasites within the cyst are called bradyzoites. The
cyst is round or oval, 10–20 μm in size and contains numerous bradyzoites. When
raw or under cooked meat containing the cysts is ingested, infection occurs. The cyst
wall is destroyed by gastric digestion and zoites which are released initiate infection
by invading intestinal epithelial cells. The zoites reach various tissues and organs
through blood and lymphatic dissemination and form tissue cysts. Cysts are suscep-
tible to freezing, thawing and heat above 60 °C.
Life Cycle (Fig. 7.2)
(1) Oocysts are passed out in faeces of cat. (2) The oocysts are ingested by rodents
and follow the life cycle to (3) form tissue cysts. (4) The definitive host (cat) ingests
tissue cyst present in intermediate host. (5) The oocysts ingested by other intermedi-
ate hosts (e.g. sheep and pig) will follow the life cycle and become tissue cysts. (6)
Humans acquire infection when they ingest uncooked meat containing tissue cysts
or ingestion of oocysts via (7) drinking contaminated water or eating unwashed
fruits and vegetables. (8) Humans can also acquire infection via blood transfusion,
(9-10) organ transplant or (11) congenital infection.