Page 177 - Basic _ Clinical Pharmacology ( PDFDrive )
P. 177
CHAPTER 10 Adrenoceptor Antagonist Drugs 163
O CH 2 CH CH 2 NH CH(CH ) O CH 2 CH CH 2 NH CH(CH )
3 2
3 2
OH OH
CH 2 CH 2 O CH 3
Propranolol Metoprolol
O CH 2 CH CH 2 NH CH(CH ) O CH 2 CH CH 2 NH C(CH )
3 2
3 3
OH O N OH
N N
S
N
Timolol
H
Pindolol
HO CH CH 2 NH CH CH 2 CH 2 O CH 2 CH CH 2 NH CH(CH )
3 2
CH 3 OH
O
C NH 2 O
OH CH 2 C NH 2
Labetalol Atenolol
OH OH
O O
CH CH 2 NH CH 2 CH
F F
Nebivolol
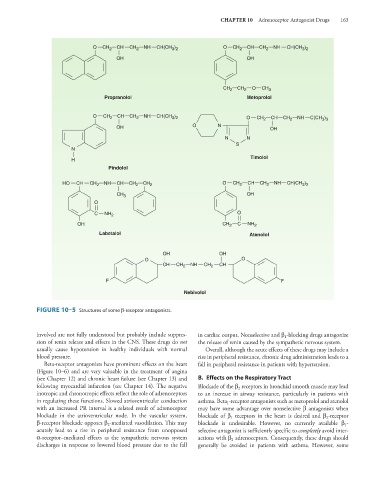
FIGURE 10–5 Structures of some β-receptor antagonists.
involved are not fully understood but probably include suppres- in cardiac output. Nonselective and β -blocking drugs antagonize
1
sion of renin release and effects in the CNS. These drugs do not the release of renin caused by the sympathetic nervous system.
usually cause hypotension in healthy individuals with normal Overall, although the acute effects of these drugs may include a
blood pressure. rise in peripheral resistance, chronic drug administration leads to a
Beta-receptor antagonists have prominent effects on the heart fall in peripheral resistance in patients with hypertension.
(Figure 10–6) and are very valuable in the treatment of angina
(see Chapter 12) and chronic heart failure (see Chapter 13) and B. Effects on the Respiratory Tract
following myocardial infarction (see Chapter 14). The negative Blockade of the β receptors in bronchial smooth muscle may lead
2
inotropic and chronotropic effects reflect the role of adrenoceptors to an increase in airway resistance, particularly in patients with
in regulating these functions. Slowed atrioventricular conduction asthma. Beta -receptor antagonists such as metoprolol and atenolol
1
with an increased PR interval is a related result of adrenoceptor may have some advantage over nonselective β antagonists when
blockade in the atrioventricular node. In the vascular system, blockade of β receptors in the heart is desired and β -receptor
2
1
β-receptor blockade opposes β -mediated vasodilation. This may blockade is undesirable. However, no currently available β -
2
1
acutely lead to a rise in peripheral resistance from unopposed selective antagonist is sufficiently specific to completely avoid inter-
α-receptor–mediated effects as the sympathetic nervous system actions with β adrenoceptors. Consequently, these drugs should
2
discharges in response to lowered blood pressure due to the fall generally be avoided in patients with asthma. However, some