Page 58 - CFCM Jan-Feb-2021_Neat
P. 58
PLATING AND ANODIZING: STACK TESTING
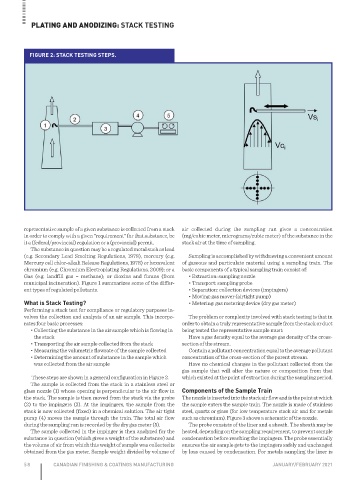
FIGURE 2: STACK TESTING STEPS.
representative sample of a given substance is collected from a stack air collected during the sampling run gives a concentration
in order to comply with a given “requirement” for that substance, be (mg/cubic meter, micrograms/cubic meter) of the substance in the
it a (federal/provincial) regulation or a (provincial) permit. stack air at the time of sampling.
The substance in question may be a regulated metal such as lead
(e.g. Secondary Lead Smelting Regulations, 1978), mercury (e.g. Sampling is accomplished by withdrawing a convenient amount
Mercury cell chlor-alkali Release Regulations, 1978) or hexavalent of gaseous and particulate material using a sampling train. The
chromium (e.g. Chromium Electroplating Regulations, 2009); or a basic components of a typical sampling train consist of:
Gas (e.g. landfill gas – methane); or dioxins and furans (from • Extraction: sampling nozzle
municipal incineration). Figure 1 summarizes some of the differ- • Transport: sampling probe
ent types of regulated pollutants. • Separation: collection devices (impingers)
• Moving: gas mover (airtight pump)
What is Stack Testing? • Metering: gas metering device (dry gas meter)
Performing a stack test for compliance or regulatory purposes in-
volves the collection and analysis of an air sample. This incorpo- The problem or complexity involved with stack testing is that in
rates four basic processes: order to obtain a truly representative sample from the stack or duct
• Collecting the substance in the air sample which is flowing in being tested the representative sample must:
the stack Have a gas density equal to the average gas density of the cross-
• Transporting the air sample collected from the stack section of the stream.
• Measuring the volumetric flowrate of the sample collected Contain a pollutant concentration equal to the average pollutant
• Determining the amount of substance in the sample which concentration of the cross-section of the parent stream.
was collected from the air sample Have no chemical changes in the pollutant collected from the
gas sample that will alter the nature or composition from that
These steps are shown in a general configuration in Figure 2. which existed at the point of extraction during the sampling period.
The sample is collected from the stack in a stainless steel or
glass nozzle (1) whose opening is perpendicular to the air flow in Components of the Sample Train
the stack. The sample is then moved from the stack via the probe The nozzle is inserted into the stack air flow and is the point at which
(2) to the impingers (3). At the impingers, the sample from the the sample enters the sample train. The nozzle is made of stainless
stack is now collected (fixed) in a chemical solution. The air tight steel, quartz or glass (for low temperature stack air and for metals
pump (4) moves the sample through the train. The total air flow such as chromium). Figure 3 shows a schematic of the nozzle.
during the sampling run is recorded by the dry gas meter (5). The probe consists of the liner and a sheath. The sheath may be
The sample collected in the impinger is then analyzed for the heated, depending on the sampling requirement, to prevent sample
substance in question (which gives a weight of the substance) and condensation before reaching the impingers. The probe essentially
the volume of air from which this weight of sample was collected is ensures the air sample gets to the impingers safely and unchanged
obtained from the gas meter. Sample weight divided by volume of by loss caused by condensation. For metals sampling the liner is
58 CANADIAN FINISHING & COATINGS MANUFACTURING JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2021