Page 337 - Programmable Logic Controllers, Fifth Edition
P. 337
uses individual controllers to control the subsystems
of a machine or process. This approach contrasts with Processor Com Network Processor Com
centralized control in which a single controller gov- Switch/Hub
erns the entire operation. A second major use of local
area networks is that of supervisory control and data
acquisition (SCADA). A LAN allows data collection
and processing for a group of controllers to be accom- Com Com
plished using one host computer as the central point for Processor Processor
collecting data.
There are three general levels of functionality of indus-
trial networks. Figure 14-27 shows an illustration of the
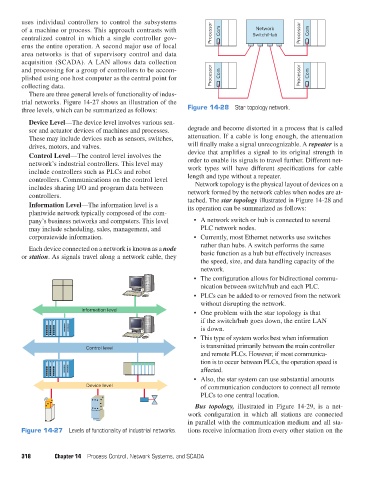
three levels, which can be summarized as follows: Figure 14-28 Star topology network.
Device Level—The device level involves various sen-
sor and actuator devices of machines and processes. degrade and become distorted in a process that is called
These may include devices such as sensors, switches, attenuation. If a cable is long enough, the attenuation
drives, motors, and valves. will finally make a signal unrecognizable. A repeater is a
Control Level—The control level involves the device that amplifies a signal to its original strength in
network’s industrial controllers. This level may order to enable its signals to travel further. Different net-
include controllers such as PLCs and robot work types will have different specifications for cable
controllers. Communications on the control level length and type without a repeater.
includes sharing I/O and program data between Network topology is the physical layout of devices on a
controllers. network formed by the network cables when nodes are at-
tached. The star topology illustrated in Figure 14-28 and
Information Level—The information level is a its operation can be summarized as follows:
plantwide network typically composed of the com-
pany’s business networks and computers. This level • A network switch or hub is connected to several
may include scheduling, sales, management, and PLC network nodes.
corporatewide information. • Currently, most Ethernet networks use switches
Each device connected on a network is known as a node rather than hubs. A switch performs the same
or station. As signals travel along a network cable, they basic function as a hub but effectively increases
the speed, size, and data handling capacity of the
network.
• The configuration allows for bidirectional commu-
nication between switch/hub and each PLC.
• PLCs can be added to or removed from the network
without disrupting the network.
Information level
• One problem with the star topology is that
if the switch/hub goes down, the entire LAN
is down.
• This type of system works best when information
Control level is transmitted primarily between the main controller
and remote PLCs. However, if most communica-
tion is to occur between PLCs, the operation speed is
affected.
• Also, the star system can use substantial amounts
Device level of communication conductors to connect all remote
PLCs to one central location.
Bus topology, illustrated in Figure 14-29, is a net-
work configuration in which all stations are connected
in parallel with the communication medium and all sta-
Figure 14-27 Levels of functionality of industrial networks. tions receive information from every other station on the
318 Chapter 14 Process Control, Network Systems, and SCADA
pet73842_ch14_305-332.indd 318 05/11/15 4:27 PM