Page 7 - Sample_test_Float
P. 7
Functions and Pointers 7
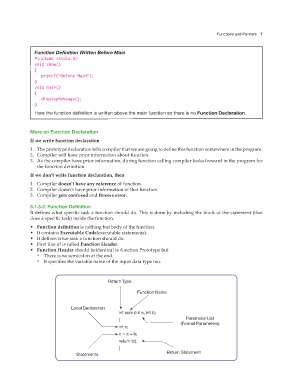
Function Definition Written Before Main
#include <stdio.h>
void show()
{
printf(“Before Main”);
}
void main()
{
displayMessage();
}
Here the function definition is written above the main function so there is no Function Declaration.
More on Function Declaration
If we write function declaration
1. The prototype declaration tells compiler that we are going to define this function somewhere in the program.
2. Compiler will have prior information about function.
3. As the compiler have prior information, during function calling compiler looks forward in the program for
the function definition.
If we don’t write function declaration, then
1. Compiler doesn’t have any reference of function.
2. Compiler doesn’t have prior information of that function.
3. Compiler gets confused and throws error.
5.1.5.2. Function Definition
It defines what specific task a function should do. This is done by including the block of the statement (that
does a specific task) inside the function.
• Function definition is nothing but body of the function.
• It contains Executable Code(executable statements).
• It defines what task a function should do.
• First line of is called Function Header.
• Function Header should beidentical to function Prototype but
◦ There is no semicolon at the end.
◦ It specifies the variable name of the input data type too.
Return Type
Function Name
Local Declaration
int sum (int a, int b)
{ Parameter List
(Formal Parameters)
int c;
c = a + b;
return (c);
}
Statements Return Statement