Page 355 - From GMS to LTE
P. 355
VoLTE, VoWifi and Mission Critical Communication 341
Internet
LTE
SGi HSS
SGi
MME voice packets
S-GW
PDN-GW SGi Cx
LTE I-CSCF
Gx Mw
Cx
PCRF Rx P-CSCF Mw S-CSCF
ISC
Sh
MMTEL
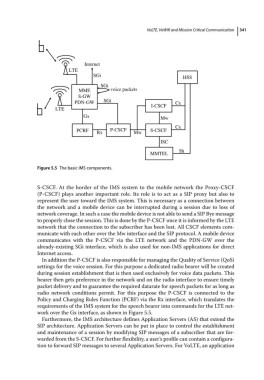
Figure 5.5 The basic IMS components.
S‐CSCF. At the border of the IMS system to the mobile network the Proxy‐CSCF
(P‐CSCF) plays another important role. Its role is to act as a SIP proxy but also to
represent the user toward the IMS system. This is necessary as a connection between
the network and a mobile device can be interrupted during a session due to loss of
network coverage. In such a case the mobile device is not able to send a SIP Bye message
to properly close the session. This is done by the P‐CSCF once it is informed by the LTE
network that the connection to the subscriber has been lost. All CSCF elements com-
municate with each other over the Mw interface and the SIP protocol. A mobile device
communicates with the P‐CSCF via the LTE network and the PDN‐GW over the
already‐existing SGi interface, which is also used for non‐IMS applications for direct
Internet access.
In addition the P‐CSCF is also responsible for managing the Quality of Service (QoS)
settings for the voice session. For this purpose a dedicated radio bearer will be created
during session establishment that is then used exclusively for voice data packets. This
bearer then gets preference in the network and on the radio interface to ensure timely
packet delivery and to guarantee the required datarate for speech packets for as long as
radio network conditions permit. For this purpose the P‐CSCF is connected to the
Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF) via the Rx interface, which translates the
requirements of the IMS system for the speech bearer into commands for the LTE net-
work over the Gx interface, as shown in Figure 5.5.
Furthermore, the IMS architecture defines Application Servers (AS) that extend the
SIP architecture. Application Servers can be put in place to control the establishment
and maintenance of a session by modifying SIP messages of a subscriber that are for-
warded from the S‐CSCF. For further flexibility, a user’s profile can contain a configura-
tion to forward SIP messages to several Application Servers. For VoLTE, an application