Page 69 - From GMS to LTE
P. 69
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) 55
Presentation (CLIP) supplementary service is active for this subscriber and not
suppressed by the Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) option that can be set
by the caller (see Table 1.4).
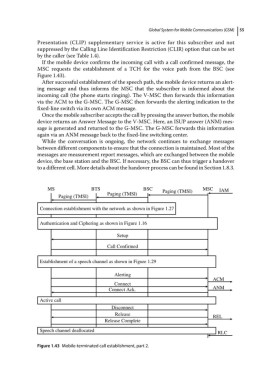
If the mobile device confirms the incoming call with a call confirmed message, the
MSC requests the establishment of a TCH for the voice path from the BSC (see
Figure 1.43).
After successful establishment of the speech path, the mobile device returns an alert-
ing message and thus informs the MSC that the subscriber is informed about the
incoming call (the phone starts ringing). The V‐MSC then forwards this information
via the ACM to the G‐MSC. The G‐MSC then forwards the alerting indication to the
fixed‐line switch via its own ACM message.
Once the mobile subscriber accepts the call by pressing the answer button, the mobile
device returns an Answer Message to the V‐MSC. Here, an ISUP answer (ANM) mes-
sage is generated and returned to the G‐MSC. The G‐MSC forwards this information
again via an ANM message back to the fixed‐line switching center.
While the conversation is ongoing, the network continues to exchange messages
between different components to ensure that the connection is maintained. Most of the
messages are measurement report messages, which are exchanged between the mobile
device, the base station and the BSC. If necessary, the BSC can thus trigger a handover
to a different cell. More details about the handover process can be found in Section 1.8.3.
MS BTS BSC Paging (TMSI) MSC IAM
Paging (TMSI)
Paging (TMSI)
Connection establishment with the network as shown in Figure 1.27
Authentication and Ciphering as shown in Figure 1.16
Setup
Call Confirmed
Establishment of a speech channel as shown in Figure 1.29
Alerting
ACM
Connect
Connect Ack. ANM
Active call
Disconnect
Release REL
Release Complete
Speech channel deallocated RLC
Figure 1.43 Mobile‐terminated call establishment, part 2.