Page 428 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 428
Network Management and Administration 3-219
2 3
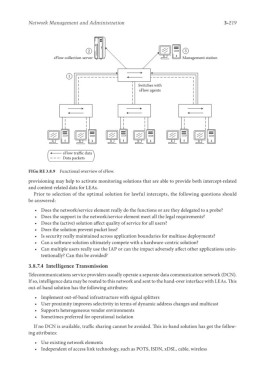
sFlow collection server Management station
1
Switches with
sFlow agents
sFlow traffic data
Data packets
FIGu RE 3.8.9 Functional overview of sFlow.
provisioning may help to activate monitoring solutions that are able to provide both intercept-related
and content-related data for LEAs.
Prior to selection of the optimal solution for lawful intercepts, the following questions should
be answered:
• Does the network/service element really do the functions or are they delegated to a probe?
• Does the support in the network/service element meet all the legal requirements?
• Does the (active) solution affect quality of service for all users?
• Does the solution prevent packet loss?
• Is security really maintained across application boundaries for multiuse deployments?
• Can a software solution ultimately compete with a hardware-centric solution?
• Can multiple users really use the IAP or can the impact adversely affect other applications unin-
tentionally? Can this be avoided?
3.8.7.4 Intelligence Transmission
Telecommunications service providers usually operate a separate data communication network (DCN).
If so, intelligence data may be routed to this network and sent to the hand-over interface with LEAs. This
out-of-band solution has the following attributes:
• Implement out-of-band infrastructure with signal splitters
• User proximity improves selectivity in terms of dynamic address changes and multicast
• Supports heterogeneous vendor environments
• Sometimes preferred for operational isolation
If no DCN is available, traffic sharing cannot be avoided. This in-band solution has got the follow-
ing attributes:
• Use existing network elements
• Independent of access link technology, such as POTS, ISDN, xDSL, cable, wireless