Page 536 - Handbook of Modern Telecommunications
P. 536
Network Organization and Governance 4-67
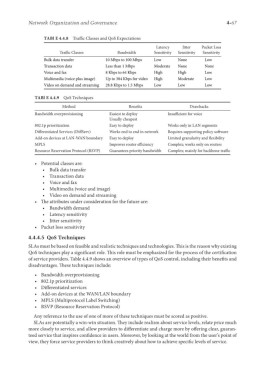
TABl E 4.4.8 Traffic Classes and QoS Expectations
Latency Jitter Packet Loss
Traffic Classes Bandwidth Sensitivity Sensitivity Sensitivity
Bulk data transfer 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps Low None Low
Transaction data Less than 1 Mbps Moderate None None
Voice and fax 8 Kbps to 64 Kbps High High Low
Multimedia (voice plus image) Up to 384 Kbps for video High Moderate Low
Video on demand and streaming 28.8 Kbps to 1.5 Mbps Low Low Low
TABl E 4.4.9 QoS Techniques
Method Benefits Drawbacks
Bandwidth overprovisioning Easiest to deploy Insufficient for voice
Usually cheapest
802.1p prioritization Easy to deploy Works only in LAN segments
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) Works end to end in network Requires supporting policy software
Add-on devices at LAN-WAN boundary Easy to deploy Limited granularity and flexibility
MPLS Improves router efficiency Complex; works only on routers
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) Guarantees priority bandwidth Complex; mainly for backbone traffic
• Potential classes are:
• Bulk data transfer
• Transaction data
• Voice and fax
• Multimedia (voice and image)
• Video on demand and streaming
• The attributes under consideration for the future are:
• Bandwidth demand
• Latency sensitivity
• Jitter sensitivity
• Packet loss sensitivity
4.4.4.5 QoS Techniques
SLAs must be based on feasible and realistic techniques and technologies. This is the reason why existing
QoS techniques play a significant role. This role must be emphasized for the process of the certification
of service providers. Table 4.4.9 shows an overview of types of QoS control, including their benefits and
disadvantages. These techniques include:
• Bandwidth overprovisioning
• 802.1p prioritization
• Differentiated services
• Add-on devices at the WAN/LAN boundary
• MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching)
• RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol)
Any reference to the use of one of more of these techniques must be scored as positive.
SLAs are potentially a win-win situation. They include realism about service levels, relate price much
more closely to service, and allow providers to differentiate and charge more by offering clear, guaran-
teed service that inspires confidence in users. Moreover, by looking at the world from the user’s point of
view, they force service providers to think creatively about how to achieve specific levels of service.