Page 280 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 280
Genetically Modified Food Cell from
Bacterium another organism
Organic farming represents one pathway toward sustainable
agriculture. Biotechnology—the application of biological sci- Nucleus
ence to create products derived from organisms—represents DNA
another. While organic agriculture seeks to scale down 1 2
the intensity of industrial agriculture in order to lessen its
impacts, biotechnology seeks to scale up the technologi- Bacterial
cal aspects of agriculture in order to produce more food at chromosome
less expense, and to reduce environmental impacts through Plasmid Gene of
enhanced efficiency. interest
The Green Revolution enabled us to feed a greater num-
ber and proportion of the world’s people, but today relent-
less population growth is demanding still more innovation. A 3 Recombinant
new set of potential solutions began to arise in the 1980s and DNA
1990s as advances in genetics enabled scientists to directly
alter the genes of organisms, including crop plants and live-
stock. The genetic modification of organisms that provide us 4
food holds promise to enhance nutrition and the efficiency
of agriculture while lessening impacts on environmental sys- Bacterium with
tems. However, genetic modification may also pose risks that recombinant
plasmid
are not yet fully understood, and the increasing role of bio-
technology in agriculture has strengthened the influence of
multinational corporations over farmers and our food supply.
For these reasons, agricultural biotechnology has inspired Cell division and
anxiety and protest by consumer advocates, small farmers, 5 reproduction
environmental advocates, and critics of big business.
We can genetically modify organisms 6 Gene transfer to
The genetic modification of crops and livestock creates geneti- target organism
cally modified organisms (GMOs) from which we derive geneti-
cally modified (GM) foods. As we learned in our Central Case
Study, GMOs result from genetic engineering, any process in
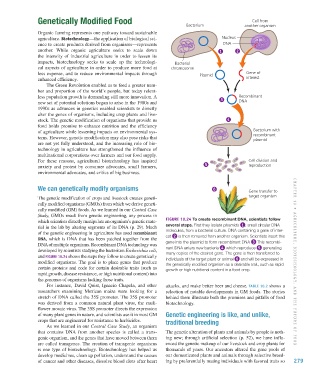
which scientists directly manipulate an organism’s genetic mate- Figure 10.24 To create recombinant DNA, scientists follow
rial in the lab by altering segments of its DNA (p. 29). Much several steps. First they isolate plasmids 1 , small circular DNA
of the genetic engineering in agriculture has used recombinant molecules, from a bacterial culture. DNA containing a gene of inter-
dNA, which is DNA that has been patched together from the est 2 is then removed from another organism. Scientists insert this
DNA of multiple organisms. Recombinant DNA technology was gene into the plasmid to form recombinant DNA 3 This recombi-
developed by scientists studying the bacterium Escherichia coli, nant DNA enters new bacteria 4 which reproduce 5 generating
many copies of the desired gene. The gene is then transferred to
and Figure 10.24 shows the steps they follow to create genetically individuals of the target plant or animal 6 and will be expressed in
modified organisms. The goal is to place genes that produce the genetically modified organism as a desirable trait, such as rapid CHAPTER 10 • A g R i C ulT u RE , Bi o TECH nology, A nd THE Fu T u RE o F Food
certain proteins and code for certain desirable traits (such as growth or high nutritional content in a food crop.
rapid growth, disease resistance, or high nutritional content) into
the genomes of organisms lacking those traits.
For instance, David Quist, Ignacio Chapela, and other attacks, and make better beer and cheese. Table 10.2 shows a
researchers examining Mexican maize were looking for a selection of notable developments in GM foods. The stories
stretch of DNA called the 35S promoter. The 35S promoter behind them illustrate both the promises and pitfalls of food
was derived from a common natural plant virus, the cauli- biotechnology.
flower mosaic virus. The 35S promoter directs the expression
of many plant genes in nature, and scientists use it in most GM Genetic engineering is like, and unlike,
crops that are engineered for resistance to herbicides. traditional breeding
As we learned in our Central Case Study, an organism
that contains DNA from another species is called a trans- The genetic alteration of plants and animals by people is noth-
genic organism, and the genes that have moved between them ing new; through artificial selection (p. 52), we have influ-
are called transgenes. The creation of transgenic organisms enced the genetic makeup of our livestock and crop plants for
is one type of biotechnology. Biotechnology has helped us thousands of years. Our ancestors altered the gene pools of
develop medicines, clean up pollution, understand the causes our domesticated plants and animals through selective breed-
of cancer and other diseases, dissolve blood clots after heart ing by preferentially mating individuals with favored traits so 279
M10_WITH7428_05_SE_C10.indd 279 12/12/14 2:59 PM