Page 683 - Basic College Mathematics with Early Integers
P. 683
9.5 VOLUME AND SURFACE AREA
Objective
Find the Volume and Surface
Area of Solids.
Objective Finding Volume and Surface Area of Solids
A convex solid is a set of points, S, not all in one plane, such that for any two points
A and B in S, all points between A and B are also in S. In this section, we will find
the volume and surface area of special types of solids called polyhedrons. A solid
formed by the intersection of a finite number of planes is called a polyhedron. The
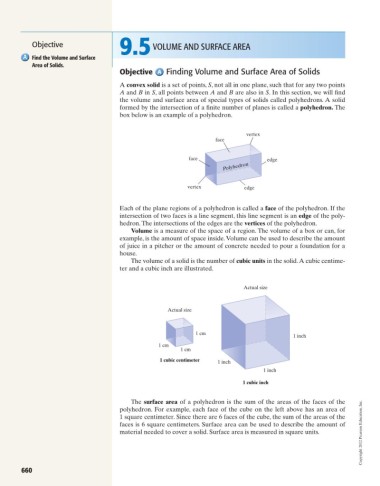
box below is an example of a polyhedron.
vertex
face
face edge
Polyhedron
vertex edge
Each of the plane regions of a polyhedron is called a face of the polyhedron. If the
intersection of two faces is a line segment, this line segment is an edge of the poly-
hedron.The intersections of the edges are the vertices of the polyhedron.
Volume is a measure of the space of a region. The volume of a box or can, for
example, is the amount of space inside. Volume can be used to describe the amount
of juice in a pitcher or the amount of concrete needed to pour a foundation for a
house.
The volume of a solid is the number of cubic units in the solid.A cubic centime-
ter and a cubic inch are illustrated.
Actual size
Actual size
1 cm
1 inch
1 cm
1 cm
1 cubic centimeter 1 inch
1 inch
1 cubic inch
The surface area of a polyhedron is the sum of the areas of the faces of the
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
polyhedron. For example, each face of the cube on the left above has an area of
1 square centimeter. Since there are 6 faces of the cube, the sum of the areas of the
faces is 6 square centimeters. Surface area can be used to describe the amount of
material needed to cover a solid. Surface area is measured in square units.
660