Page 70 - Basic College Mathematics with Early Integers
P. 70
1.6 MULTIPLYING WHOLE NUMBERS AND AREA Objectives
Use the Properties of
Multiplication.
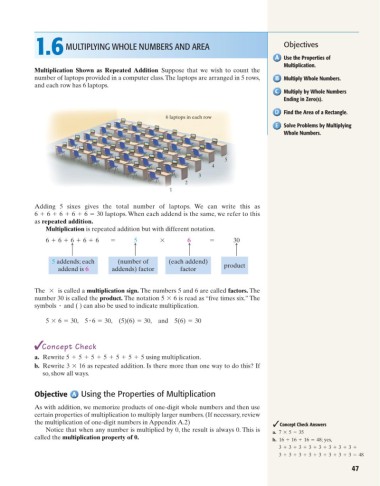
Multiplication Shown as Repeated Addition Suppose that we wish to count the
number of laptops provided in a computer class.The laptops are arranged in 5 rows, Multiply Whole Numbers.
and each row has 6 laptops.
Multiply by Whole Numbers
Ending in Zero(s).
Find the Area of a Rectangle.
6 laptops in each row
Solve Problems by Multiplying
Whole Numbers.
5
4
3
2
1
Adding 5 sixes gives the total number of laptops. We can write this as
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 30 laptops. When each addend is the same, we refer to this
as repeated addition.
Multiplication is repeated addition but with different notation.
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 5 * 6 = 30
æ æ æ æ
5 addends; each (number of (each addend)
product
addend is 6 addends) factor factor
The * is called a multiplication sign. The numbers 5 and 6 are called factors. The
number 30 is called the product. The notation 5 * 6 is read as “five times six.” The
#
symbols and ( ) can also be used to indicate multiplication.
#
5 * 6 = 30, 5 6 = 30, (5)(6) = 30, and 5(6) = 30
Concept Check
a. Rewrite 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 using multiplication.
b. Rewrite 3 * 16 as repeated addition. Is there more than one way to do this? If
so, show all ways.
Objective Using the Properties of Multiplication
As with addition, we memorize products of one-digit whole numbers and then use
certain properties of multiplication to multiply larger numbers. (If necessary, review
the multiplication of one-digit numbers in Appendix A.2)
Concept Check Answers
Notice that when any number is multiplied by 0, the result is always 0. This is
a. 7 * 5 = 35
called the multiplication property of 0.
b. 16 + 16 + 16 = 48; yes,
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 +
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 48
47