Page 454 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 454
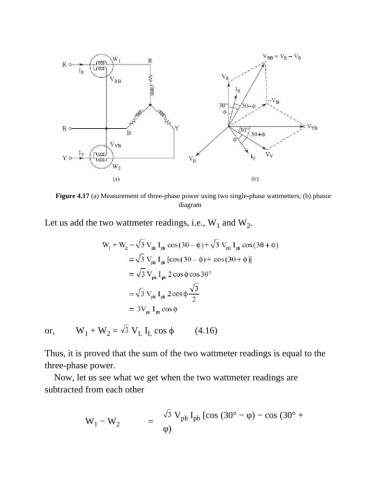
Figure 4.17 (a) Measurement of three-phase power using two single-phase wattmetters; (b) phasor
diagram
Let us add the two wattmeter readings, i.e., W and W .
1
2
or, W + W = V I cos ϕ (4.16)
1
L L
2
Thus, it is proved that the sum of the two wattmeter readings is equal to the
three-phase power.
Now, let us see what we get when the two wattmeter readings are
subtracted from each other
V I [cos (30° − φ) − cos (30° +
ph ph
W − W 2 =
1
φ)