Page 12 - RTH3BA Preview
P. 12
R���� T����� �������� - B������� �� A������� 3 �� E������.
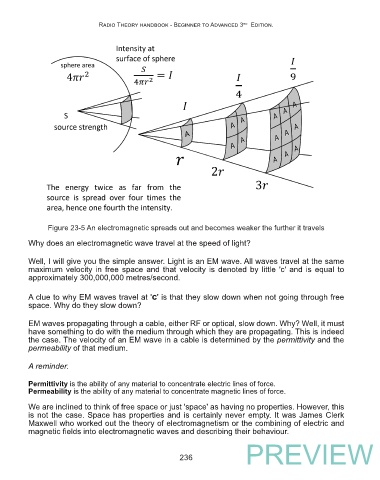
Figure 23-5 An electromagnetic spreads out and becomes weaker the further it travels
Why does an electromagnetic wave travel at the speed of light?
Well, I will give you the simple answer. Light is an EM wave. All waves travel at the same
maximum velocity in free space and that velocity is denoted by little 'c' and is equal to
approximately 300,000,000 metres/second.
A clue to why EM waves travel at 'c' is that they slow down when not going through free
space. Why do they slow down?
EM waves propagating through a cable, either RF or optical, slow down. Why? Well, it must
have something to do with the medium through which they are propagating. This is indeed
the case. The velocity of an EM wave in a cable is determined by the permittivity and the
permeability of that medium.
A reminder.
Permittivity is the ability of any material to concentrate electric lines of force.
Permeability is the ability of any material to concentrate magnetic lines of force.
We are inclined to think of free space or just 'space' as having no properties. However, this
is not the case. Space has properties and is certainly never empty. It was James Clerk
Maxwell who worked out the theory of electromagnetism or the combining of electric and
magnetic fields into electromagnetic waves and describing their behaviour.
PREVIEW
236