Page 5 - FINAL CFA I SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 2
P. 5
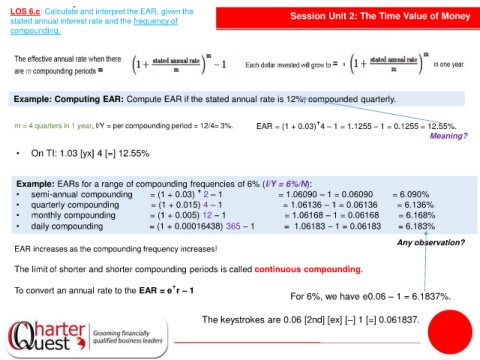
LOS 6.c: Calculate and interpret the EAR, given the Session Unit 2: The Time Value of Money
stated annual interest rate and the frequency of
compounding.
Example: Computing EAR: Compute EAR if the stated annual rate is 12%, compounded quarterly.
m = 4 quarters in 1 year, I/Y = per compounding period = 12/4= 3%. EAR = (1 + 0.03)ꜛ4 – 1 = 1.1255 – 1 = 0.1255 = 12.55%.
Meaning?
• On TI: 1.03 [yx] 4 [=] 12.55%
Example: EARs for a range of compounding frequencies of 6% (I/Y = 6%/N):
• semi-annual compounding = (1 + 0.03) ꜛ 2 – 1 = 1.06090 – 1 = 0.06090 = 6.090%
• quarterly compounding = (1 + 0.015) 4 – 1 = 1.06136 – 1 = 0.06136 = 6.136%
• monthly compounding = (1 + 0.005) 12 – 1 = 1.06168 – 1 = 0.06168 = 6.168%
• daily compounding = (1 + 0.00016438) 365 – 1 = 1.06183 – 1 = 0.06183 = 6.183%
Any observation?
EAR increases as the compounding frequency increases!
The limit of shorter and shorter compounding periods is called continuous compounding.
To convert an annual rate to the EAR = eꜛr – 1
For 6%, we have e0.06 – 1 = 6.1837%.
The keystrokes are 0.06 [2nd] [ex] [–] 1 [=] 0.061837.