Page 102 - Microsoft Word - 00 IWB ACCA F7.docx
P. 102
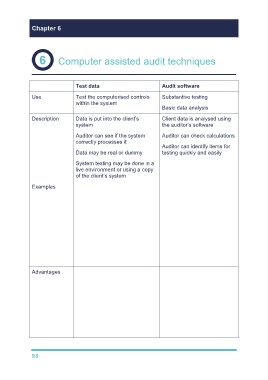
Chapter 6 3 4
Computer assisted audit techniques
Test data Audit software
Use Test the computerised controls Substantive testing
within the system
Basic data analysis
Description Data is put into the client’s Client data is analysed using
system the auditor’s software
Auditor can see if the system Auditor can check calculations
correctly processes it
Auditor can identify items for
Data may be real or dummy testing quickly and easily
System testing may be done in a
live environment or using a copy
of the client’s system
Examples The auditor enters data e.g. Re-performance of
addition or ageing of
A timesheet with hours invoices
outside the normal range to
check that the system Identifying items for
rejects it. testing e.g. identify credit
balances on the
A customer order that will receivables ledger
exceed the credit limit to
ensure the system rejects it. Preparation of reports
Calculations of ratios
Sample selection
Advantages Enables the auditor to test Calculations and casting
programmed controls which of reports will be quicker.
wouldn't otherwise be able
to be tested. More transactions can be
tested
Once designed, costs
incurred will be minimal Computer files rather
unless the programmed than printouts are tested
controls are changed Cost effective once set
requiring the test data to be up
redesigned.
98