Page 263 - FM Integrated WorkBook STUDENT 2018-19
P. 263
Interest rate risk
Why interest rates fluctuate
2.1 The yield curve
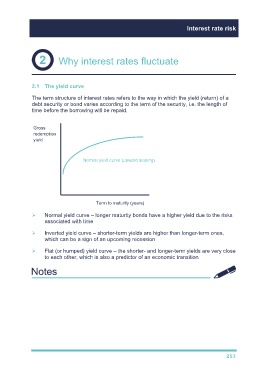
The term structure of interest rates refers to the way in which the yield (return) of a
debt security or bond varies according to the term of the security, i.e. the length of
time before the borrowing will be repaid.
Gross
redemption
yield
Normal yield curve (upward sloping)
Term to maturity (years)
Normal yield curve – longer maturity bonds have a higher yield due to the risks
associated with time
Inverted yield curve – shorter-term yields are higher than longer-term ones,
which can be a sign of an upcoming recession
Flat (or humped) yield curve – the shorter- and longer-term yields are very close
to each other, which is also a predictor of an economic transition
253