Page 64 - FINAL CFA SLIDES DECEMBER 2018 DAY 14
P. 64
Session Unit 14:
Valuing a Bond Using Forward Rates
52. Introduction To Fixed Income Valuation
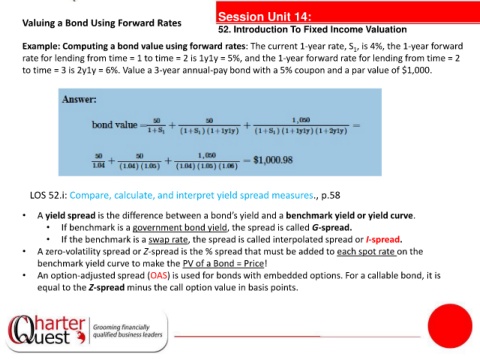
Example: Computing a bond value using forward rates: The current 1-year rate, S , is 4%, the 1-year forward
1
rate for lending from time = 1 to time = 2 is 1y1y = 5%, and the 1-year forward rate for lending from time = 2
to time = 3 is 2y1y = 6%. Value a 3-year annual-pay bond with a 5% coupon and a par value of $1,000.
tanties
LOS 52.i: Compare, calculate, and interpret yield spread measures., p.58
• A yield spread is the difference between a bond’s yield and a benchmark yield or yield curve.
• If benchmark is a government bond yield, the spread is called G-spread.
• If the benchmark is a swap rate, the spread is called interpolated spread or I-spread.
• A zero-volatility spread or Z-spread is the % spread that must be added to each spot rate on the
benchmark yield curve to make the PV of a Bond = Price!
• An option-adjusted spread (OAS) is used for bonds with embedded options. For a callable bond, it is
equal to the Z-spread minus the call option value in basis points.