Page 23 - PM Integrated Workbook 2018-19
P. 23
A revision of Management Accounting (MA) topics
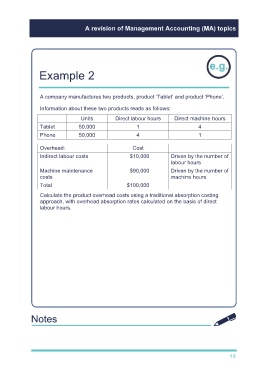
Example 2
A company manufactures two products, product ‘Tablet’ and product ‘Phone’.
Information about these two products reads as follows:
Units Direct labour hours Direct machine hours
Tablet 50,000 1 4
Phone 50,000 4 1
Overhead: Cost
Indirect labour costs $10,000 Driven by the number of
labour hours
Machine maintenance $90,000 Driven by the number of
costs machine hours
Total $100,000
Calculate the product overhead costs using a traditional absorption costing
approach, with overhead absorption rates calculated on the basis of direct
labour hours.
Using a traditional absorption costing approach, the OAR may be calculated
for each production cost centre as total overheads divided by total labour
hours:
$100,000
OAR =
{ 1 × 50,000 + 4 × 50,000 }
OAR = $0.40 per labour hour.
Under traditional absorption costing, overheads would be absorbed into the
two products as follows:
Overheads absorbed into product ‘Tablet’: 1 hour × $0.40 = $0.40
Overheads absorbed into product ‘Phone’: 4 hours × $0.40 = $1.60
15