Page 36 - PM Integrated Workbook 2018-19
P. 36
Chapter 2
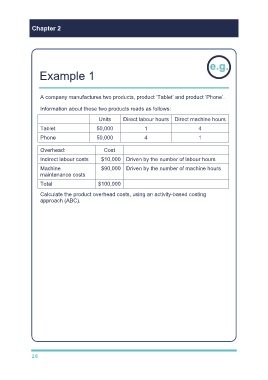
Example 1
A company manufactures two products, product ‘Tablet’ and product ‘Phone’.
Information about these two products reads as follows:
Units Direct labour hours Direct machine hours
Tablet 50,000 1 4
Phone 50,000 4 1
Overhead: Cost
Indirect labour costs $10,000 Driven by the number of labour hours
Machine $90,000 Driven by the number of machine hours
maintenance costs
Total $100,000
Calculate the product overhead costs, using an activity-based costing
approach (ABC).
Using ABC, each different activity has its own absorption rate.
Therefore, in the example above, if labour and machining are the major
activities of the business, and the factors which drive the cost of the activities
are labour hours and machine hours, absorption rates would be calculated as
follows:
$10,000
Indirect labour costs absorption rate = OAR =
{ 1 × 50,000 + 4 × 50,000 }
$10,000
OAR =
250,000 labour hours
OAR = $0.04 per direct labour hour
$90,000
Machine maintenance costs absorption rate =OAR=
{ 4 × 50,000 + 1 × 50,000 }
$90,000
OAR =
250,000 machine hours
OAR = $0.36 per machine hour
28