Page 40 - Anemia Hemolitica No autoinmune
P. 40
Infección
632 Part V Red Blood Cells
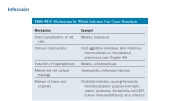
Table 45-2 Mechanisms by Which Infection Can Cause Hemolysis
Mechanism
Direct parasitization of red cells
Immune mechanisms
Induction of hypersplenism
Altered red cell surface topology
Release of toxins and enzymes
Example
Malaria, babesiosis
Cold agglutinin hemolysis after infectious mononucleosis or mycoplasmal pneumonia (see Chapter 44)
Malaria, schistosomiasis Haemophilus influenzae infection
Clostridial infection causing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura–hemolytic uremic syndrome, Escherichia coli 0197, human immunodeficiency virus infection
question of w ously infected merozoite rho infection was sitized erythr fected RBCs d probably are tion, particula function that
The lifespa normal RBCs a shorter lifes persist after c be removed f of pitting, p potentially e parasitemia.
Other inf
p a
o n
p l r
r x
e include Carrió