Page 36 - Compilation of Worksheets1
P. 36
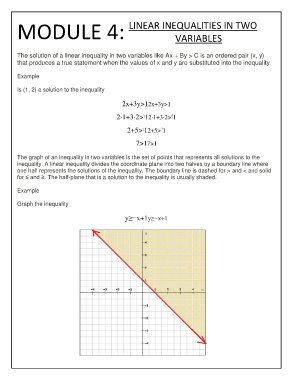
MODULE 4: LINEAR INEQUALITIES IN TWO
VARIABLES
The solution of a linear inequality in two variables like Ax + By > C is an ordered pair (x, y)
that produces a true statement when the values of x and y are substituted into the inequality.
Example
Is (1, 2) a solution to the inequality
2x+3y>12x+3y>1
?
2⋅1+3⋅2> 12⋅1+3⋅2> 1
?
?
2+5> 12+5> 1
?
7>17>1
The graph of an inequality in two variables is the set of points that represents all solutions to the
inequality. A linear inequality divides the coordinate plane into two halves by a boundary line where
one half represents the solutions of the inequality. The boundary line is dashed for > and < and solid
for ≤ and ≥. The half-plane that is a solution to the inequality is usually shaded.
Example
Graph the inequality
y≥−x+1y≥−x+1