Page 48 - SITHCCC014_SG_v1.0
P. 48
P a g e | 48
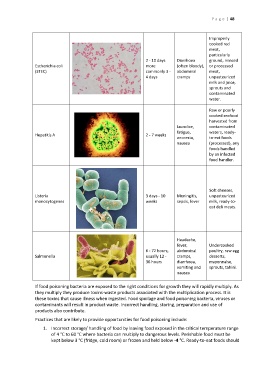
Improperly
cooked red
meat,
particularly
2 - 10 days Diarrhoea ground, minced
Escherichia coli more (often bloody), or processed
(STEC) commonly 3 - abdominal meat,
4 days cramps unpasteurized
milk and juice,
sprouts and
contaminated
water.
Raw or poorly
cooked seafood
harvested from
Jaundice, contaminated
fatigue, waters, ready-
Hepatitis A 2 - 7 weeks
anorexia, to-eat foods
nausea (processed), any
foods handled
by an infected
food handler.
Soft cheeses,
Listeria 3 days - 10 Meningitis, unpasteurized
monocytogenes weeks sepsis, fever milk, ready-to-
eat deli meats.
Headache,
fever, Undercooked
6 - 72 hours, abdominal poultry, raw egg
Salmonella usually 12 - cramps, desserts,
36 hours diarrhoea, mayonnaise,
vomiting and sprouts, tahini.
nausea
If food poisoning bacteria are exposed to the right conditions for growth they will rapidly multiply. As
they multiply they produce toxins-waste products associated with the multiplication process. It is
these toxins that cause illness when ingested. Food spoilage and food poisoning bacteria, viruses or
contaminants will result in product waste. Incorrect handling, storing, preparation and use of
products also contribute.
Practices that are likely to provide opportunities for food poisoning include:
1. Incorrect storage/ handling of food by leaving food exposed in the critical temperature range
of 4 °C to 60 °C where bacteria can multiply to dangerous levels. Perishable food must be
kept below 3 °C (fridge, cold room) or frozen and held below -4 °C. Ready-to-eat foods should