Page 31 - BAHASA PEMROGRAMAN C++
P. 31
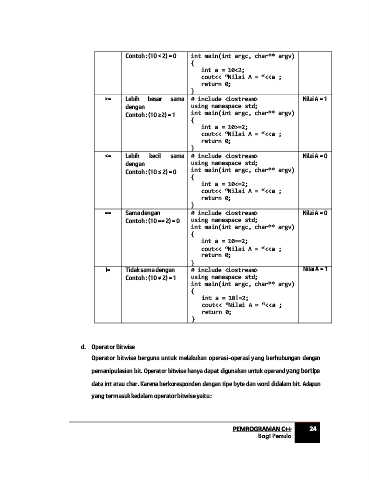
Contoh : (10 < 2) = 0 int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int a = 10<2;
cout<< “Nilai A = “<<a ;
return 0;
}
>= Lebih besar sama # include <iostream> Nilai A = 1
dengan using namespace std;
Contoh : (10 ≥2) = 1 int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int a = 10>=2;
cout<< “Nilai A = “<<a ;
return 0;
}
<= Lebih kecil sama # include <iostream> Nilai A = 0
dengan using namespace std;
Contoh : (10 ≤ 2) = 0 int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int a = 10<=2;
cout<< “Nilai A = “<<a ;
return 0;
}
== Sama dengan # include <iostream> Nilai A = 0
Contoh : (10 == 2) = 0 using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int a = 10==2;
cout<< “Nilai A = “<<a ;
return 0;
}
!= Tidak sama dengan # include <iostream> Nilai A = 1
Contoh : (10 ≠ 2) = 1 using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int a = 10!=2;
cout<< “Nilai A = “<<a ;
return 0;
}
d. Operator Bitwise
Operator bitwise berguna untuk melakukan operasi-operasi yang berhubungan dengan
pemanipulasian bit. Operator bitwise hanya dapat digunakan untuk operand yang bertipe
data int atau char. Karena berkoresponden dengan tipe byte dan word didalam bit. Adapun
yang termasuk kedalam operator bitwise yaitu :
PEMROGRAMAN C++ 24
Bagi Pemula
24