Page 87 - PBL71 OI/AXM630-EN AZTEC 600 SS (WIRO)
P. 87
Aztec 600 ISE ammonia and fluoride
Single-stream ion-selective analyzers Appendix D – Principle of Operation – Fluoride Analyzers
Appendix D – Principle of Operation – Fluoride Analyzers
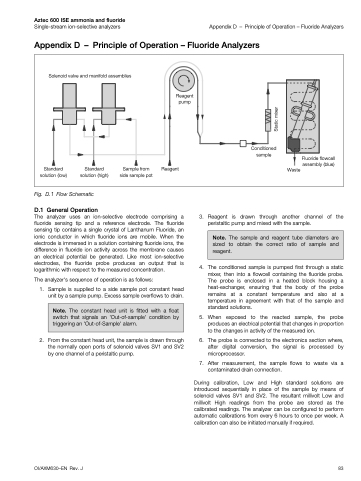
Solenoid valve and manifold assemblies
Reagent pump
Reagent
Conditioned sample
Fluoride flowcell
assembly (blue) Waste
Standard solution (low)
Standard solution (high)
Sample from side sample pot
Fig. D.1 Flow Schematic
D.1 General Operation
The analyzer uses an ion-selective electrode comprising a fluoride sensing tip and a reference electrode. The fluoride sensing tip contains a single crystal of Lanthanum Fluoride, an ionic conductor in which fluoride ions are mobile. When the electrode is immersed in a solution containing fluoride ions, the difference in fluoride ion activity across the membrane causes an electrical potential be generated. Like most ion-selective electrodes, the fluoride probe produces an output that is logarithmic with respect to the measured concentration.
The analyzer's sequence of operation is as follows:
1. Sample is supplied to a side sample pot constant head unit by a sample pump. Excess sample overflows to drain.
2. From the constant head unit, the sample is drawn through the normally open ports of solenoid valves SV1 and SV2 by one channel of a peristaltic pump.
3. Reagent is drawn through another channel of the peristaltic pump and mixed with the sample.
4. The conditioned sample is pumped first through a static mixer, then into a flowcell containing the fluoride probe. The probe is enclosed in a heated block housing a heat-exchanger, ensuring that the body of the probe remains at a constant temperature and also at a temperature in agreement with that of the sample and standard solutions.
5. When exposed to the reacted sample, the probe produces an electrical potential that changes in proportion to the changes in activity of the measured ion.
6. The probe is connected to the electronics section where, after digital conversion, the signal is processed by microprocessor.
7. After measurement, the sample flows to waste via a contaminated drain connection.
During calibration, Low and High standard solutions are introduced sequentially in place of the sample by means of solenoid valves SV1 and SV2. The resultant millivolt Low and millivolt High readings from the probe are stored as the calibrated readings. The analyzer can be configured to perform automatic calibrations from every 6 hours to once per week. A calibration can also be initiated manually if required.
OI/AXM630–EN Rev. J
83
Note. The sample and reagent tube diameters are sized to obtain the correct ratio of sample and reagent.
Note. The constant head unit is fitted with a float switch that signals an 'Out-of-sample' condition by triggering an 'Out-of-Sample' alarm.
Static mixer