Page 50 - Green Builder Magazine Nov-Dec 2017 Issue
P. 50
Effects of Additives, Fillers and
Reinforcements on Polymer Properties
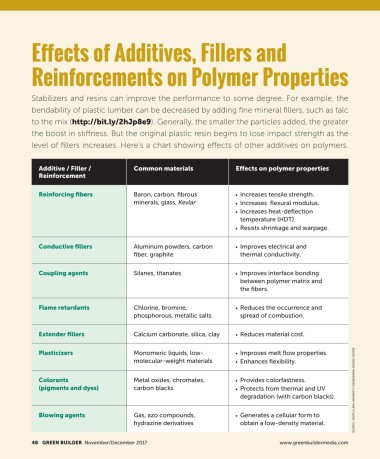
Stabilizers and resins can improve the performance to some degree. For example, the
bendability of plastic lumber can be decreased by adding fine mineral fillers, such as talc
to the mix (http://bit.ly/2hJp8e9). Generally, the smaller the particles added, the greater
the boost in stiffness. But the original plastic resin begins to lose impact strength as the
level of fillers increases. Here’s a chart showing effects of other additives on polymers.
Additive / Filler / Common materials Effects on polymer properties
Reinforcement
Reinforcing fibers Baron, carbon, fibrous ■ ■ Increases tensile strength.
minerals, glass, Kevlar ■ ■ Increases flexural modulus.
■ Increases heat-deflection
■
temperature (HDT).
■ Resists shrinkage and warpage.
■
Conductive fillers Aluminum powders, carbon ■ ■ Improves electrical and
fiber, graphite thermal conductivity.
Coupling agents Silanes, titanates ■ ■ Improves interface bonding
between polymer matrix and
the fibers.
Flame retardants Chlorine, bromine, ■ ■ Reduces the occurrence and
phosphorous, metallic salts spread of combustion.
Extender fillers Calcium carbonate, silica, clay ■ ■ Reduces material cost.
SOURCE: SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DESIGN CENTER
Plasticizers Monomeric liquids, low- ■ ■ Improves melt flow properties.
molecular-weight materials ■ ■ Enhances flexibility.
Colorants Metal oxides, chromates, ■ ■ Provides colorfastness.
(pigments and dyes) carbon blacks ■ Protects from thermal and UV
■
degradation (with carbon blacks).
Blowing agents Gas, azo compounds, ■ ■ Generates a cellular form to
hydrazine derivatives obtain a low-density material.
48 GREEN BUILDER November/December 2017 www.greenbuildermedia.com
44-51 GB 1117 Perils of Plastic.indd 48 11/17/17 11:32 AM