Page 107 - Design in Nature
P. 107
Reactive Swimming Systems 105
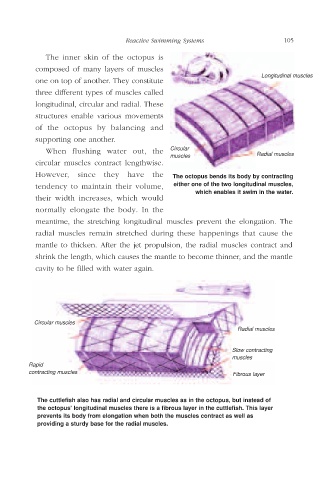
The inner skin of the octopus is
composed of many layers of muscles
Longitudinal muscles
one on top of another. They constitute
three different types of muscles called
longitudinal, circular and radial. These
structures enable various movements
of the octopus by balancing and
supporting one another.
When flushing water out, the Circular
muscles Radial muscles
circular muscles contract lengthwise.
However, since they have the The octopus bends its body by contracting
tendency to maintain their volume, either one of the two longitudinal muscles,
which enables it swim in the water.
their width increases, which would
normally elongate the body. In the
meantime, the stretching longitudinal muscles prevent the elongation. The
radial muscles remain stretched during these happenings that cause the
mantle to thicken. After the jet propulsion, the radial muscles contract and
shrink the length, which causes the mantle to become thinner, and the mantle
cavity to be filled with water again.
Circular muscles
Radial muscles
Slow contracting
muscles
Rapid
contracting muscles Fibrous layer
The cuttlefish also has radial and circular muscles as in the octopus, but instead of
the octopus' longitudinal muscles there is a fibrous layer in the cuttlefish. This layer
prevents its body from elongation when both the muscles contract as well as
providing a sturdy base for the radial muscles.