Page 2 - FONCITRIL
P. 2
Potassium Citrate
• Increases Urinary PH
• Increases Urinary Citrate levels
Citric Acid
• Increases Urinary PH
• Increases Urinary Citrate levels
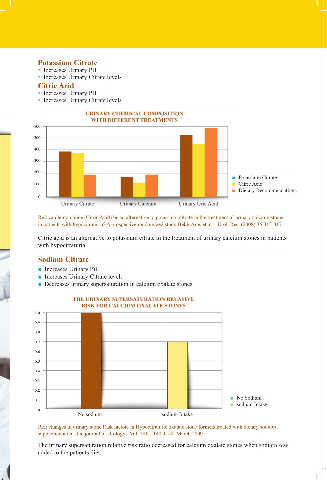
URINARY CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
WITH DIFFERENT TREATMENTS
600
500
400
300
200 ■ Potassium Citrate
■ Citric Acid
100 ■ Dietary Recommendations
0 Urinary Calcium Urinary Uric Acid
Urinary Citrate
Ref: can lemon juice (Citric Acid) be an alternative to potassium citrate in the treatment of urinary calcium stones
in patients with hypocitraturia? A prospective randomized study Bekir Aras et al. - Urol. Res. (2008) 36:313-317
Citric acid is an alternative to potassium citrate in the treatment of urinary calcium stones in patients
with hypocitraturia.
Sodium Citrate
■ Increases Urinary PH
■ Increases Urinary Citrate levels
■ Decreases urinary supersaturation in calcium oxalate stones
THE URINARY SUPERSATURATION RELATIVE
RISK FOR CALCIUM OXALATE STONES
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1 ■ No Sodium
■ sodium Intake
0 sodium Intake
No sodium
Ref: changes in urinary stone Risk factors in Hypocitraturic oxalate stone formers treated with dietary sodium
supplementaion - the journal of Urology - Vol. 181, 1140-1144, March 2009
The urinary supersaturation relative risk ratio decreased for calcium oxalate stones when sodium was
added to the patients diet.