Page 150 - ro membanes
P. 150
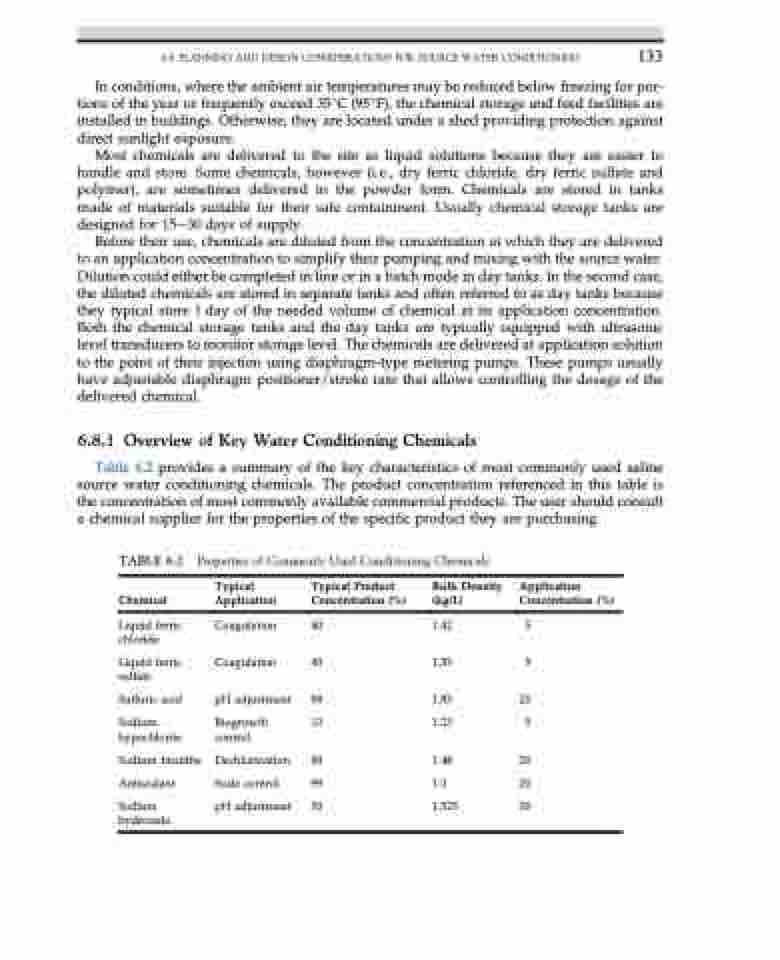
TABLE 6.2
Chemical
Liquid ferric chloride
Liquid ferric sulfate
Sulfuric acid
Sodium hypochlorite
Sodium bisulfite Antiscalant
Sodium hydroxide
6.8 PLANNING AND DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR SOURCE WATER CONDITIONING 133
In conditions, where the ambient air temperatures may be reduced below freezing for por- tions of the year or frequently exceed 35C (95F), the chemical storage and feed facilities are installed in buildings. Otherwise, they are located under a shed providing protection against direct sunlight exposure.
Most chemicals are delivered to the site as liquid solutions because they are easier to handle and store. Some chemicals, however (i.e., dry ferric chloride, dry ferric sulfate and polymer), are sometimes delivered in the powder form. Chemicals are stored in tanks made of materials suitable for their safe containment. Usually chemical storage tanks are designed for 15e30 days of supply.
Before their use, chemicals are diluted from the concentration at which they are delivered to an application concentration to simplify their pumping and mixing with the source water. Dilution could either be completed in line or in a batch mode in day tanks. In the second case, the diluted chemicals are stored in separate tanks and often referred to as day tanks because they typical store 1 day of the needed volume of chemical at its application concentration. Both the chemical storage tanks and the day tanks are typically equipped with ultrasonic level transducers to monitor storage level. The chemicals are delivered at application solution to the point of their injection using diaphragm-type metering pumps. These pumps usually have adjustable diaphragm positioner/stroke rate that allows controlling the dosage of the delivered chemical.
6.8.1 Overview of Key Water Conditioning Chemicals
Table 6.2 provides a summary of the key characteristics of most commonly used saline source water conditioning chemicals. The product concentration referenced in this table is the concentration of most commonly available commercial products. The user should consult a chemical supplier for the properties of the specific product they are purchasing.
Properties of Commonly Used Conditioning Chemicals
Typical Application
Coagulation Coagulation
pH adjustment
Biogrowth control
Dechlorination Scale control pH adjustment
Typical Product Concentration (%)
40 40
98 13
99 99 50
Bulk Density (kg/L)
1.42 1.55
1.83 1.23
1.48 1.0 1.525
Application Concentration (%)
5
5
20 5
20 20 20