Page 35 - WOM_SUMMER_FEB
P. 35
948
dental materials 3 3 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 944–953
Table 3 – Modified USPHS criteria for direct clinical evaluation (van Dijken [44]).
Score
Criteria
Category
Unacceptable
Acceptable
Anatomical form
0
Slightly under- or over-contoured restoration; marginal ridges slightly
1
undercontoured; contact slightly open (may be self-correcting);
occlusal height reduced locally
Restoration is undercontoured, dentin or base exposed; contact is
2
faulty, not self-correcting; occlusal height reduced; occlusion affected
Restoration is missing partially or totally; fracture of tooth structure;
3
shows traumatic occlusion; restoration causes pain in tooth or
adjacent tissue
Marginal adaptation
0
Restoration is contiguous with existing anatomic form, explorer does
not catch
1
Explorer catches, no crevice is visible into which explorer will
penetrate
2
Crevice at margin, enamel exposed
3
Obvious crevice at margin, dentin or base exposed
4
restoration mobile, fractured or missing
Very good color match
0
Color match
Good color match
1
2
Slight mismatch in color, shade or translucency
Obvious mismatch, outside the normal range
3
4
Gross mismatch
Marginal
0
No discoloration evident
Slight staining, can be polished away
1
discoloration
2
Obvious staining can not be polished away
3
Gross staining
Surface roughness
0
Smooth surface
Slightly rough or pitted
1
2
Rough, cannot be refinished
Surface deeply pitted, irregular grooves
3
0
No evidence of caries contiguous with the margin of the restoration
Caries
Caries is evident contiguous with the margin of the restoration
1
female participants. Sixteen participants were estimated as
main disadvantages is that polymerization after light irra-
having high caries risk and nineteen showed mild to severe
diation never is completed and continues at least another
parafunctional habits during the observation period. Five of
24 hours. Uncured comomoners and additives released by
seven caries lesions were observed in high caries risk par-
diffusion through dentin into the pulp and by saliva, will
ticipants and eight of eleven fractures (cusp and material)
remain in the surrounding tissues and become bioavailable for
occurred in bruxing participants.
metabolism [14]. Apart from the elution of residual monomers
and additives immediately after placement, diverse chem-
ical reactions like solvolysis (enzymatical), hydrolysis, and
4.
Discussion
alcoholysis as well as physical processes like wear and ero-
sion promote a constant disintegration and dissolution of
resin polymers. TEGDMA and HEMA are probably the two
Dental resin composites are complex mixed materials, which
co-monomers that contribute most to the severe cytotoxic
consist of an organic polymerizable matrix, reinforcing fillers,
effects and allergic reactions. [18,42,48]. Reichl et al showed
a silane coupling agent and various additives. One of their The restoration is contiguous with tooth anatomy
Table 4 – Not-acceptable restorations and reasons for failure during the 6 years follow up. cmf = cmf/els, ASE = AdheSE
One F/els, RC = resin composite.
1 year 2 year 3 year 4 year 5 year 6 year Total dental materials 3 3 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 944–953 949
cmf ASE cmf ASE cmf ASE cmf ASE cmf ASE cmf ASE
RC fracture 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 9
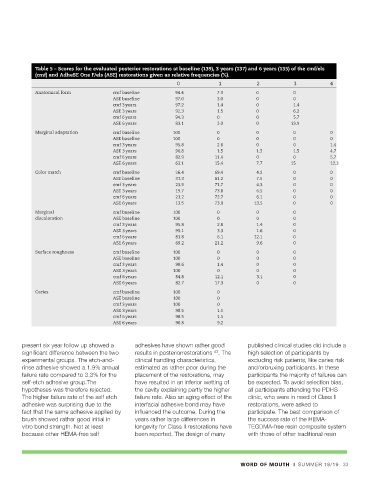
RC fracture and caries 2 2 4 Table 5 – Scores for the evaluated posterior restorations at baseline (139), 3 years (137) and 6 years (135) of the cmf/els
(cmf) and AdheSE One F/els (ASE) restorations given as relative frequencies (%).
Caries 1 1 1 1 4
Cusp fracture 1 2 1 4 0 1 2 3 4
Cumulative absolute frequencies 0 2 1 3 2 5 4 9 6 11 8 13 21 Anatomical form cmf baseline 94.4 7.3 0 0
Cumulative relative frequencies (%) 0 3.0 1.4 4.5 2.8 7.7 5.7 13.9 8.6 16.9 11.4 20.0 ASE baseline 97.0 3.0 0 0
cmf 3 years 97.2 1.4 0 1.4
ASE 3 years 92.3 1.5 0 6.2
cmf 6 years 94.3 0 0 5.7
by diffusion through dent in into the ring-opening polymerization process al showed that of several investigated ASE 6 years 83.1 3.0 0 13.9
pulp and by saliva, will remain in the which reduced the volume shrinkage adhesive systems, cmf used in this Marginal adaptation cmf baseline 100 0 0 0 0
surrounding tissues and become to less than 1%. A meta-analysis of 11 study was the only adhesive which did ASE baseline 100 0 0 0 0
14
bioavailable for metabolism . Apart clinical studies showed acceptable not release HEMA and TEGDMA. They cmf 3 years 95.8 2.8 0 0 1.4
from the elution of residual performance for the silorane-based reported that the above discussed ASE 3 years 90.8 1.5 1.5 1.5 4.7
monomersand additives immediately material and similarly to methacrylate- silorane adhesive system released cmf 6 years 82.9 11.4 0 7.7 15 0 5.7
ASE 6 years
15.4
12.3
63.1
after placement, diverse chemical based resin composites . The both HEMAand TEGDMA. This resin
12
reactions like solvolysis (enzymatical), authors concluded that low composite system was recently Color match cmf baseline 26.4 69.4 4.2 0 0 0 0
31.3
61.2
ASE baseline
7.5
hydrolysis, and alcoholysis as well as polymerization was not the most withdrawn from the market. Reichl et cmf 3 years 23.9 71.7 4.3 0 0
physical processes like wear and important factor deciding the clinical al concluded that cmf can be used as ASE 3 years 19.7 73.8 6.5 0 0
erosion promote a constant effectiveness of a resin composite adhesive system for patients with cmf 6 years 21.2 72.7 6.1 0 0
disintegration and dissolution of resin system in posterior cavities. It has diagnosed allergies for HEMA and/or ASE 6 years 13.5 73.0 13.5 0 0
polymers. TEGDMA and HEMA are been suggested for many years that TEGDMA. Mine et al. reported that Marginal cmf baseline 100 0 0 0
49
probably the two co-monomers that stress generation at tooth/resin the adhesive showed good discoloration ASE baseline 100 0 0 0
contribute most to the severe composite interfaces and the resulting microtensile bond strength to enamel, cmf 3 years 95.8 2.8 1.4 0
1.6
cytotoxic effects and allergic interfacial deficiencies remain one of but significantly lower to dentin ASE 3 years 95.1 3.3 12.1 0 0
81.8
6.1
cmf 6 years
reactions. 18,42,48 . Reichl et al showed the most important reasons forclinical compared to the golden standard ASE 6 years 69.2 21.2 9.6 0
that unpolymerized TEGDMA and failure . The claim that minimizing the 3-step etch-and-rinse Optibond FL. Surface roughness cmf baseline 100 0 0 0
40
HEMA remain chemically and shrinkage stresses may lead to They concluded that the overall ASE baseline 100 0 0 0
physically unchanged and can leach improvements in the success rateand bonding effectiveness of the new cmf 3 years 98.6 1.4 0 0
up to 30d . It has been stated that survival of restorations can be found in adhesive was reasonable and ASE 3 years 100 0 0 0
42
for biocompatibility reasons these many scientificarticles 50,51 . However, comparable with bond strengths cmf 6 years 84.8 12.1 3.1 0
monomers should be avoided in clinical evidence has been missing recorded for other recently marketed ASE 6 years 82.7 17.3 0 0
dental biomaterials, especially in that shrinkage stress plays such an adhesives tested in the sameway . Caries cmf baseline 100 0
49
10
patients with diagnosed allergies . To important clinical role .The Longevity results of restorations ASE baseline 100 0
49
replace thesemonomers in resin investigated resin composite in this placed in Class V non-carious lesions cmf 3 years 100 0 1.5
98.5
ASE 3 years
composite systems have been the study, with both low shrinkage and showed also that the clinical retention cmf 6 years 98.5 1.5
goal of novel research projects . low shrinkage stress but also with low of the studied TEGDMA/HEMA-free ASE 6 years 90.8 9.2
38
Several HEMA-free adhesives have flexural strength, flexural modulus, and adhesive in low stress bearing
been marketed during the last years compressive strength [ 40,43 ],showed localizations was highly acceptable that unpolymerized TEGDMA and HEMA remain chemically not the most important factor deciding the clinical effec-
tiveness of a resin composite system in posterior cavities. It
and physically unchanged and can leach up to 30d [42].
and acceptable clinical retention and good clinical durability. The low annual and in line with the better etch-and- present six year follow up showed a adhesives have shown rather good published clinical studies did include a
has been suggested for many years that stress generation at
It has been stated that for biocompatibility reasons these
43
durability have been shown for some failure rates observed were similar but rinse adhesives . The Class II significant difference between the two results in posteriorrestorations . The high selection of participants by
43
monomers should be avoided in dental biomaterials, espe-
tooth/resin composite interfaces and the resulting interfacial
of these products in Class V NCCL´ıs, not superior to those observed in restoration is the most stress bearing experimental groups. The etch-and- clinical handling characteristics, excluding risk patients, like caries risk
deficiencies remain one of the most important reasons for
cially in patients with diagnosed allergies [49]. To replace these
and also in posterior restoration other studies of several resin restoration. The present six year rinse adhesive showed a 1.9% annual estimated as rather poor during the and/orbruxing participants. In these
monomers in resin composite systems have been the goal of
clinical failure [40]. The claim that minimizing the shrink-
studies . However, the TEGDMA composites with higher shrink-age results were obtained for extensive failure rate compared to 3.3% for the placement of the restorations, may participants the majority of failures can
43
age stresses may lead to improvements in the success rate
novel research projects [38]. Several HEMA-free adhesives have
monomer and other low molecular stress 40,52,53 . This finding is in Class II restorations. Class I self-etch adhesive group.The have resulted in an inferior wetting of be expected. To avoid selection bias,
been marketed during the last years and acceptable clinical
and survival of restorations can be found in many scientific
weight monomers are still used in agreement with the statement in restorations were not included as have hypotheses was therefore rejected. the cavity explaining partly the higher all participants attending the PDHS
articles [50,51] However, clinical evidence has been missing
retention and durability have been shown for some of these
41
most marketed resin composites .A Magno et al´ıs meta-analysis and been the case in many earlier The higher failure rate of the self etch failure rate. Also an aging effect of the clinic, who were in need of Class II
products in Class V NCCL´ ıs, and also in posterior restoration
that shrinkage stress plays such an important clinical role [10].
restorations, were asked to
new methacrylate-free resin earlier reported findings, that low posterior resin composite studies. adhesive was surprising due to the interfacial adhesive bond may have resin composite in this study, with both low
studies [43]. However, the TEGDMA monomer and other low
The investigated
composite was introducedin 2007 shrinkage stress is an important Clinical posterior restoration studies fact that the same adhesive applied by used in most marketed shrinkage and participate. The best comparison of
molecular weight monomers are still
influenced the outcome. During the low shrinkage stress but also with low flexural
the success rate of the HEMA-
based on silorane monomers with advantage and certainly plays a role including Class I restorations show brush showed rather good initial in years rather large differences in flexural modulus, and compressive strength [40,43],
strength,
resin composites [41].
TEGDMA-free resin composite system
longevity for Class II restorations have
traditional filler particles. The resin for the durability of the restoration, but lower AFR´ıs, depending on the ratio vitro bond strength. Not at least resin composite was introduced showed good clinical durability. The low annual failure rates
A new methacrylate-free
composite polymerized through a not as the main factor 10,12,54 . Reichl et Class I/Class II restorations. The because other HEMA-free self monomers with traditional filler observed were with those of other traditional resin
in 2007 based on silorane
been reported. The design of many similar but not superior to those observed in
particles. The resin composite polymerized through a ring- other studies of several resin composites with higher shrink-
opening polymerization process which reduced the volume age stress [40,52,53]. This finding is in agreement with the
shrinkage to less than 1%. A meta-analysis of 11 clinical stud- statement in Magno et al´ ıs meta-analysis and earlier reported
32 WORD OF MOUTH SUMMER 18/19 ies showed acceptable performance for the silorane-based findings, that low shrinkage stress is an important advantage 33
WORD OF MOUTH SUMMER 18/19
material and similarly to methacrylate-based resin compos- and certainly plays a role for the durability of the restoration,
ites [12]. The authors concluded that low polymerization was but not as the main factor. [10,12,54].