Page 85 - C:\Users\msi\OneDrive\Documents\Flip PDF Corporate Edition\E-Commerce\
P. 85
If elements arrive prior to the presentation deadline Dmax, due to variations in
system latencies, buffering is required to hold the element in reserve until time
tpi. Due to the deadline specification, data errors in retrieval or transmission may
not be correctable via re-retrieval or retransmission. Acceptable error rates are
application and media dependent. In order to meet the requirements of
stimulability of a continuous media stream, each subsystem must provide a
maximum delay with some probability p. Further, in order to limit buffering
requirements, the variation in delay, referred to as jitter, must also be bounded.
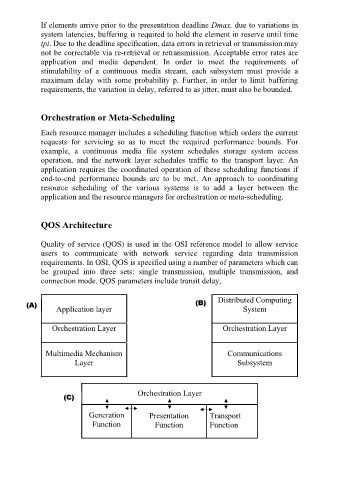
Orchestration or Meta-Scheduling
Each resource manager includes a scheduling function which orders the current
requests for servicing so as to meet the required performance bounds. For
example, a continuous media file system schedules storage system access
operation, and the network layer schedules traffic to the transport layer. An
application requires the coordinated operation of these scheduling functions if
end-to-end performance bounds are to be met. An approach to coordinating
resource scheduling of the various systems is to add a layer between the
application and the resource managers for orchestration or meta-scheduling.
QOS Architecture
Quality of service (QOS) is used in the OSI reference model to allow service
users to communicate with network service regarding data transmission
requirements. In OSI, QOS is specified using a number of parameters which can
be grouped into three sets: single transmission, multiple transmission, and
connection mode. QOS parameters include transit delay,
Distributed Computing
(A) (B)
Application layer System
Orchestration Layer Orchestration Layer
Multimedia Mechanism Communications
Layer Subsystem
(C) Orchestration Layer
Generation Presentation Transport
Function Function Function