Page 18 - Internal Auditor M.E. - June 2019
P. 18
risk Management
The Strategy Map and scorecard are collocated according to four and the effectiveness of those controls regularly assessed. The key
perspectives (although the exact number and even titles are not controls can be either preventive, that is, designed to reduce the
mandated) that are described hierarchically, with shareholder (or likelihood of the risk materializing, or detective, that is, controls
financial) at the apex and then flowing down through customer,
internal processes and learning and growth. A slightly different that are designed to detect when a risk has materialized.
hierarchy is typically used in the public sector.
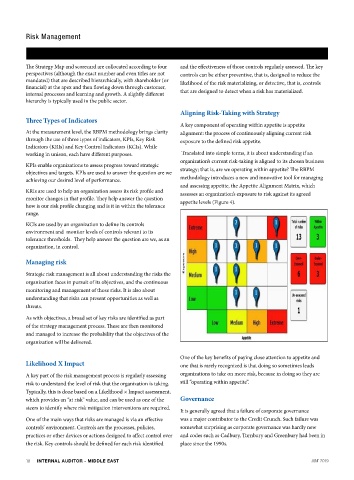
Aligning Risk-Taking with Strategy
Three Types of Indicators
A key component of operating within appetite is appetite
At the measurement level, the RBPM methodology brings clarity alignment: the process of continuously aligning current risk
through the use of three types of indicators, KPIs, Key Risk exposure to the defined risk appetite.
Indicators (KRIs) and Key Control Indicators (KCIs). While
working in unison, each have different purposes. Translated into simple terms, it is about understanding if an
organization’s current risk-taking is aligned to its chosen business
KPIs enable organizations to assess progress toward strategic
objectives and targets. KPIs are used to answer the question are we strategy; that is, are we operating within appetite? The RBPM
achieving our desired level of performance. methodology introduces a new and innovative tool for managing
and assessing appetite, the Appetite Alignment Matrix, which
KRIs are used to help an organization assess its risk profile and assesses an organization’s exposure to risk against its agreed
monitor changes in that profile. They help answer the question appetite levels (Figure 4).
how is our risk profile changing and is it in within the tolerance
range.
KCIs are used by an organization to define its controls
environment and monitor levels of controls relevant to its
tolerance thresholds. They help answer the question are we, as an
organization, in control.
Managing risk
Strategic risk management is all about understanding the risks the
organization faces in pursuit of its objectives, and the continuous
monitoring and management of those risks. It is also about
understanding that risks can present opportunities as well as
threats.
As with objectives, a broad set of key risks are identified as part
of the strategy management process. These are then monitored
and managed to increase the probability that the objectives of the
organization will be delivered.
One of the key benefits of paying close attention to appetite and
Likelihood X Impact one that is rarely recognized is that doing so sometimes leads
A key part of the risk management process is regularly assessing organizations to take on more risk, because in doing so they are
risk to understand the level of risk that the organization is taking. still “operating within appetite”.
Typically, this is done based on a Likelihood × Impact assessment,
which provides an “at risk” value, and can be used as one of the Governance
steers to identify where risk mitigation interventions are required.
It is generally agreed that a failure of corporate governance
One of the main ways that risks are managed is via an effective was a major contributor to the Credit Crunch. Such failure was
controls’ environment. Controls are the processes, policies, somewhat surprising as corporate governance was hardly new
practices or other devices or actions designed to affect control over and codes such as Cadbury, Turnbury and Greenbury had been in
the risk. Key controls should be defined for each risk identified place since the 1990s.
18 INTERNAL AUDITOR - MIDDLE EAST JUNE 2019