Page 60 - Harvard Business Review (November-December, 2017)
P. 60
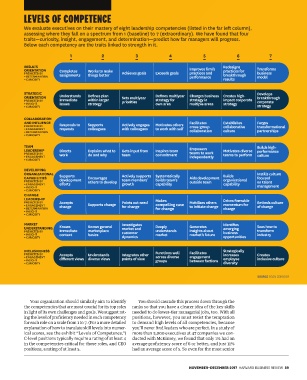
LEVELS OF COMPETENCE
We evaluate executives on their mastery of eight leadership competencies (listed in the far left column),
assessing where they fall on a spectrum from 1 (baseline) to 7 (extraordinary). We have found that four
traits—curiosity, insight, engagement, and determination—predict how far managers will progress.
Below each competency are the traits linked to strength in it.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
RESULTS Redesigns
ORIENTATION Completes Works to make Improves firm’s practices for Transforms
PREDICTED BY assignments things better Achieves goals Exceeds goals practices and breakthrough business
• DETERMINATION performance model
• CURIOSITY results
STRATEGIC Develops
ORIENTATION Understands Defines plan Sets multiyear Defines multiyear Changes business Creates high- breakthrough
PREDICTED BY immediate within larger priorities strategy for strategy in impact corporate corporate
• INSIGHT issues strategy own area multiple areas strategy
• CURIOSITY strategy
COLLABORATION
AND INFLUENCE Responds to Supports Actively engages Motivates others Facilitates Establishes Forges
PREDICTED BY cross-group collaborative transformational
• ENGAGEMENT requests colleagues with colleagues to work with self collaboration culture partnerships
• DETERMINATION
• CURIOSITY
TEAM Empowers Builds high-
LEADERSHIP Directs Explains what to Gets input from Inspires team Motivates diverse performance
PREDICTED BY work do and why team commitment teams to work teams to perform culture
• ENGAGEMENT independently
• CURIOSITY
DEVELOPING
ORGANIZATIONAL Supports Actively supports Systematically Builds Instills culture
CAPABILITIES development Encourages team members’ builds team’s Aids development organizational focused
PREDICTED BY others to develop outside team on talent
• ENGAGEMENT efforts growth capability capability management
• INSIGHT
• CURIOSITY
CHANGE
LEADERSHIP Makes Drives firmwide
PREDICTED BY Accepts Supports change Points out need compelling case Mobilizes others momentum for Embeds culture
• ENGAGEMENT change for change to initiate change of change
• DETERMINATION for change change
• INSIGHT
• CURIOSITY
MARKET Investigates Identifies
UNDERSTANDING Knows Knows general market and Deeply Generates emerging Sees how to
PREDICTED BY immediate marketplace customer understands insights about business transform
• INSIGHT context basics market market’s future industry
• CURIOSITY dynamics opportunities
INCLUSIVENESS Functions well Facilitates Strategically
PREDICTED BY Accepts Understands Integrates other increases Creates
• ENGAGEMENT different views diverse views points of view across diverse engagement employee inclusive culture
• INSIGHT groups between factions
• CURIOSITY diversity
SOURCE EGON ZEHNDER
Your organization should similarly aim to identify You should cascade this process down through the
the competencies that are most crucial for its top roles ranks so that you have a clearer idea of the key skills
in light of its own challenges and goals. We suggest rat- needed to do lower-tier managerial jobs, too. With all
ing the level of proficiency needed in each competency positions, however, you must resist the temptation
for each role on a scale from 1 to 7. (For a more detailed to demand high levels of all competencies, because
explanation of how to translate skill levels into numer- you’ll never find leaders who are perfect. In a study of
ical scores, see the exhibit “Levels of Competence.”) more than 5,000 executives at 47 companies we con-
C-level positions typically require a rating of at least 4 ducted with McKinsey, we found that only 1% had an
in the competencies critical for those roles, and CEO average proficiency score of 6 or better, and just 11%
positions, a rating of at least 5. had an average score of 5. So even for the most senior
NOVEMBER–DECEMBER 2017 HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW 89