Page 167 - omiicot_vol21
P. 167
3.1.1 Aqueous extraction
The leaves of ‘Sambung nyawa’ were extracted using aqueous extraction method, based on method by Lee et al.,
(2011). Fresh leaves of ‘Sambung nyawa’ were washed, weighed and dried in oven at temperature of 45 °C for period
of three days (3 days). Upon drying, dried leaves would be blended into powder form, then 20 g of dried leaves
powder would be mixed with 400 mL of distilled water (ratio of 1:20) and was heated in water bath (50°C) for three
hour (3 hour) with stirring of the extract at every 20 minutes interval. The extract was cooled and centrifuged at 1500
rpm for 10 minutes. Supernatant obtained was separated and the pellet was subjected to another round of
centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes. Both of the supernatants would be combined and freeze-dried to yield
brown powder of ‘Sambung nyawa’ leaves crude aqueous extract and stored in labelled bottles in chiller. Table 3.1.1
show the amount of ‘Sambung nyawa’ leaves extract used in each formulation.
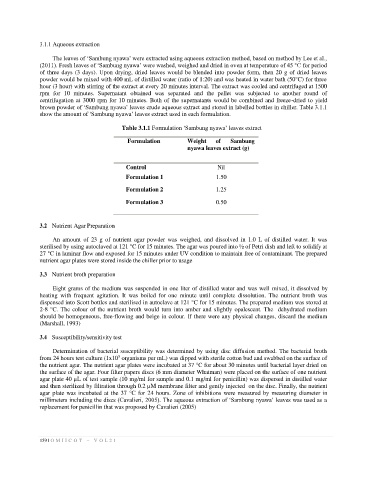
Table 3.1.1 Formulation ‘Sambung nyawa’ leaves extract
Formulation Weight of Sambung
nyawa leaves extract (g)
Control Nil
Formulation 1 1.50
Formulation 2 1.25
Formulation 3 0.50
3.2 Nutrient Agar Preparation
An amount of 23 g of nutrient agar powder was weighed, and dissolved in 1.0 L of distilled water. It was
sterilised by using autoclaved at 121 °C for 15 minutes. The agar was poured into ½ of Petri dish and left to solidify at
27 °C in laminar flow and exposed for 15 minutes under UV condition to maintain free of contaminant. The prepared
nutrient agar plates were stored inside the chiller prior to usage
3.3 Nutrient broth preparation
Eight grams of the medium was suspended in one liter of distilled water and was well mixed, it dissolved by
heating with frequent agitation. It was boiled for one minute until complete dissolution. The nutrient broth was
dispensed into Scott bottles and sterilised in autoclave at 121 °C for 15 minutes. The prepared medium was stored at
2-8 °C. The colour of the nutrient broth would turn into amber and slightly opalescent. The dehydrated medium
should be homogeneous, free-flowing and beige in colour. If there were any physical changes, discard the medium
(Marshall, 1993)
3.4 Susceptibility/sensitivity test
Determination of bacterial susceptibility was determined by using disc diffusion method. The bacterial broth
from 24 hours test culture (1x10 organisms per mL) was dipped with sterile cotton bud and swabbed on the surface of
5
the nutrient agar. The nutrient agar plates were incubated at 37 °C for about 30 minutes until bacterial layer dried on
the surface of the agar. Four filter papers discs (6 mm diameter Whatman) were placed on the surface of one nutrient
agar plate 40 µL of test sample (10 mg/ml for sample and 0.1 mg/ml for penicillin) was dispersed in distilled water
and then sterilized by filtration through 0.2 µM membrane filter and gently injected on the disc. Finally, the nutrient
agar plate was incubated at the 37 °C for 24 hours. Zone of inhibitions were measured by measuring diameter in
millimeters including the discs (Cavalieri, 2005). The aqueous extraction of ‘Sambung nyawa’ leaves was used as a
replacement for penicillin that was proposed by Cavalieri (2005)
159 | O M I I C O T – V O L 2 1