Page 21 - GAO-02-327 Electronic Government: Challenges to Effective Adoption of the Extensible Markup Language
P. 21
Chapter 1: Background: Features and Current
Federal Use of XML
However, unlike XML, HTML’s tags are predefined and are used solely to
transmit instructions for displaying information on Web pages. HTML tags
describe document structures (that is, whether text should be treated as a
heading, a list, a quotation, and so on) and document appearance (such as
whether text should be emphasized, larger or smaller than surrounding
text, or in a particular type font or color). A Web browser that receives an
HTML file simply displays the stream of data that it receives according to
the HTML instructions, without “understanding” what information it is
displaying. Table 1 summarizes the differences and similarities between
HTML and XML.
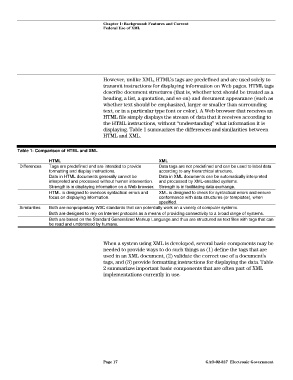
Table 1: Comparison of HTML and XML
HTML XML
Differences Tags are predefined and are intended to provide Data tags are not predefined and can be used to label data
formatting and display instructions. according to any hierarchical structure.
Data in HTML documents generally cannot be Data in XML documents can be automatically interpreted
interpreted and processed without human intervention. and processed by XML-enabled systems.
Strength is in displaying information on a Web browser. Strength is in facilitating data exchange.
HTML is designed to overlook syntactical errors and XML is designed to check for syntactical errors and ensure
focus on displaying information. conformance with data structures (or templates), when
specified.
Similarities Both are nonproprietary W3C standards that can potentially work on a variety of computer systems.
Both are designed to rely on Internet protocols as a means of providing connectivity to a broad range of systems.
Both are based on the Standard Generalized Markup Language and thus are structured as text files with tags that can
be read and understood by humans.
When a system using XML is developed, several basic components may be
needed to provide ways to do such things as (1) define the tags that are
used in an XML document, (2) validate the correct use of a document’s
tags, and (3) provide formatting instructions for displaying the data. Table
2 summarizes important basic components that are often part of XML
implementations currently in use.
Page 17 GAO-02-327 Electronic Government