Page 116 - SAPEM-Chapter-10-2nd-edition-2014
P. 116
South African Pavement Engineering Manual
Chapter 10: Pavement Design
7.8 The Asphalt Institute Surface Deflection Design Method
The Asphalt Institute (AI) method for pavement rehabilitation design uses either a pavement layer analysis or a
deflection analysis procedure. Only the deflection procedure is discussed in this section, and the discussion is taken
largely from Jordaan (1989c). This method is not routinely used in South Africa.
The primary pavement input to the method is Representative Rebound Deflection (RRD). The RDD is calculated from
the mean Benkelman beam surface deflection plus two standard deviations for the deflection data sample. A
minimum of 10 deflections at maximum intervals of 80 metres are recommended per road section. The deflection is
adjusted to a reference temperature of 21 °C at the most critical period, usually just after the rainy season. A chart
is provided for temperature adjustment of the deflection, but no guidelines are provided on the adjustment for the
critical period.
The AI surface deflection method provides design charts to estimate the remaining life of an existing pavement to
reach a terminal condition, and to determine the asphalt overlay thickness required to extend the life of the
pavement to carry the future expected traffic.
(i) Remaining Life Estimation
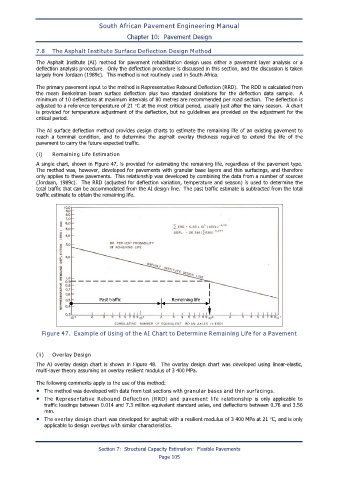
A single chart, shown in Figure 47, is provided for estimating the remaining life, regardless of the pavement type.
The method was, however, developed for pavements with granular base layers and thin surfacings, and therefore
only applies to these pavements. This relationship was developed by combining the data from a number of sources
(Jordaan, 1989c). The RRD (adjusted for deflection variation, temperature and season) is used to determine the
total traffic that can be accommodated from the AI design line. The past traffic estimate is subtracted from the total
traffic estimate to obtain the remaining life.
Past traffic Remaining life
Figure 47. Example of Using of the AI Chart to Determine Remaining Life for a Pavement
(ii) Overlay Design
The AI overlay design chart is shown in Figure 48. The overlay design chart was developed using linear-elastic,
multi-layer theory assuming an overlay resilient modulus of 3 400 MPa.
The following comments apply to the use of this method:
• The method was developed with data from test sections with granular bases and thin surfacings.
• The Representative Rebound Deflection (RRD) and pavement life relationship is only applicable to
traffic loadings between 0.014 and 7.3 million equivalent standard axles, and deflections between 0.76 and 3.56
mm.
• The overlay design chart was developed for asphalt with a resilient modulus of 3 400 MPa at 21 °C, and is only
applicable to design overlays with similar characteristics.
Section 7: Structural Capacity Estimation: Flexible Pavements
Page 105