Page 38 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 38
38 Lasers Technology | Progress Report
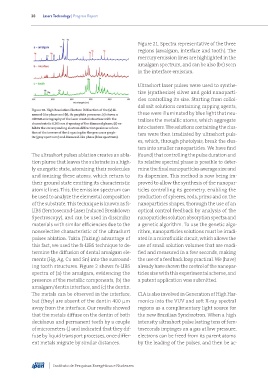
Figure 21. Spectra representative of the three
regions (amalgam, interface and tooth). The
mercury emission lines are highlighted in the
amalgam spectrum, and can be also (be) seen
in the interface emission.
Ultrashort laser pulses were used to synthe-
tize (synthesize) silver and gold nanoparti-
cles controlling its size. Starting from colloi-
dal salt solutions containing capping agents,
Figure 20. High Resolution Electron Diffraction of the (a) di-
amond-like phase and (b), its graphite precursor; (c) shows a these were illuminated by blue light that neu-
HRTEM micrography of the laser created structure with the tralizes the metallic atoms, which aggregate
characteristic 0.205 nm d-spacing of the diamond phase; (d) ex-
hibits the corresponding electron diffraction peaks as a func- into clusters. The solutions containing the clus-
tion of the inverse of the d-spacing for the precursor graph- ters were then irradiated by ultrashort puls-
ite (gray spectrum) and diamond-like phase (blue spectrum).
es, which, through photolysis, break the clus-
ters into smaller nanoparticles. We have find
The ultrashort pulses ablation creates an abla- (found) that controlling the pulse duration and
tion plume that leaves the substrate in a high- its relative spectral phase is possible to deter-
ly energetic state, atomizing their molecules mine the final nanoparticles average size and
and ionizing these atoms, which return to its dispersion. This method is now being im-
their ground state emitting its characteristic proved to allow the synthesis of the nanopar-
atomic lines. This, the emission spectrum can ticles controlling its geometry, enabling the
be used to analyze the elemental composition production of spheres, rods, prims and on the
of the substrate. This technique is known as fs- nanoparticles shapes, thorough the use of an
LIBS (femtosecond-Laser Induced Breakdown optical control feedback by analysis of the
Spectroscopy), and can be used in dissimilar nanoparticles solution absorption spectra and
materials with similar efficiencies due to the a genetic algorithm. To use the genetic algo-
nonselective characteristic of the ultrashort rithm, nanoparticles solutions must be irradi-
pulses ablation. Takin (Taking) advantage of ated in a microfluidic circuit, which allows the
this fact, we used the fs-LIBS technique to de- use of small solution volumes that are modi-
termine the diffusion of dental amalgam ele- fied and measured in a few seconds, making
ments (Hg, Ag, Cu and Sn) into the surround- the use of a feedback loop practical. We (have)
ing tooth structures. Figure 2 shows fs-LIBS already have shown the control of the nanopar-
spectra of (a) the amalgam, evidencing the ticles size with this experimental scheme, and
presence of the metallic components, (b) the a patent application was submitted.
amalgam/dentin interface, and (c) the dentin.
The metals can be observed in the interface, CLA is also involved in Generation of High Har-
but (they) are absent of the dentin 400 μm monics into the VUV and soft X-ray spectral
away from the interface. Our results showed regions as a complimentary light source for
that the metals diffuse on the dentin of both the new Brazilian Synchrotron. When a high
deciduous and permanent teeth by a couple intensity ultrashort pulse lasting tens of fem-
of micrometers (,) and indicated that they dif- toseconds impinges on a gas at low pressure,
fuse by liquid transport processes, once differ- electrons can be freed from its parent atoms
ent metals migrate by similar distances. by the leading of the pulses, and then be ac-
Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares