Page 65 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 65
Application of Ionizing Radiations | Progress Report 65
and specific site delivery. This study was per- ferent materials with characteristics achieved
formed with Dr. Gustavo Varca collaboration. by the modifying reagent. The grafting tech-
nique can be improved and yield superior re-
Controlled radical polymerization sults when it is performed in conjunction
and grafting onto polymeric with controlled radical polymerization (CRP)
substrates using ionizing radiation techniques instead of conventional free-radi-
cal polymerization methods. Among the CRP
methods, the reversible
addition–fragmentation
chain transfer (RAFT) po-
lymerization is consid-
ered as advantageous con-
sidering its applicability
to most monomers that
reacts through radical po-
lymerization, compatibil-
ity with various reaction
conditions and simplicity
of execution compared to
competitive techniques.
Glycidyl methacrylate
(GMA), has both vinyl and
epoxy functions, is a re-
active monomer which
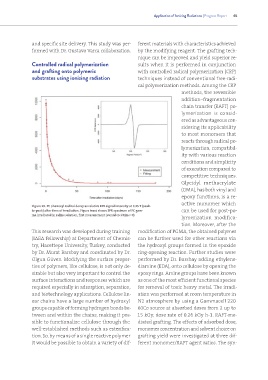
Figure 29. PC phenoxyl radical decay as relative EPR signal intensity at 0.35 T (peak-
to-peak) after time of irradiation. Figure inset shows EPR spectrum of PC gam- can be used for post-po-
ma irradiated in saline solution, first measurement (considered time=0).
lymerization modifica-
tion. Moreover, after the
This research was developed during training modification of PGMA, the obtained polymer
(IAEA fellowship) at Department of Chemis- can be further used for other reactions via
try, Hacettepe University, Turkey, conducted the hydroxyl groups formed in the epoxide
by Dr. Murat Barsbay and coordinated by Dr. ring-opening reaction. Further studies were
Olgun Güven. Modifying the surface proper- performed by Dr. Barsbay adding ethylene-
ties of polymers, like cellulose, is not only de- diamine (EDA), onto cellulose by opening the
sirable but also very important to control the epoxy rings. Amine groups have been known
surface interactions and responses which are as one of the most efficient functional species
required especially in adsorption, separation, for removal of toxic heavy metal. The irradi-
and biotechnology applications. Cellulose lin- ation was performed at room temperature in
ear chains have a large number of hydroxyl N2 atmosphere by using a Gammacell 220
groups capable of forming hydrogen bonds be- 60Co source at absorbed doses from 2 up to
tween and within the chains, making it pos- 15 kGy, dose rate of 0.26 kGy h-1. RAFT-me-
sible to functionalize cellulose through the diated grafting. The effects of adsorbed dose,
well-established methods such as esterifica- monomer concentration and solvent choice on
tion. So, by means of a single reactive polymer grafting yield were investigated at three dif-
it would be possible to obtain a variety of dif- ferent monomer/RAFT agent ratios. The syn-