Page 32 - 01. Indian Contract Act, 1872
P. 32
(iii) Death of a promisor- contracts involving personal skill or expertise of
promisor. When promisor dies, it cannot be performed by anyone else and
hence comes to an end.
(iv) Merger of rights-if an inferior right in a contract is merged into a superior
right by the party.
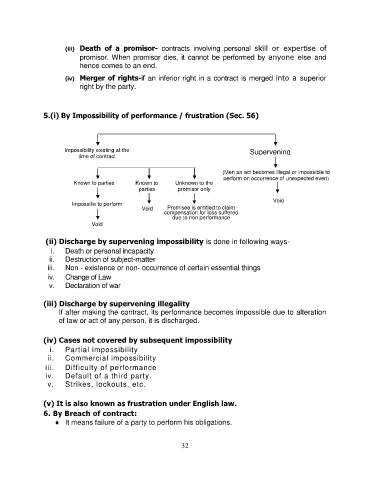
5.(i) By Impossibility of performance / frustration (Sec. 56)
Impossibility existing at the Supervening
time of contract Impossibility
(Men an act becomes illegal or impossible to
perform on occurrence of unexpected even)
Known to parties Known to Unknown to the
parties promisor only
Void
Impossille to perform Promisee is entitled to claim
Void compensation for loss suffered
due to non performance
Void
(ii) Discharge by supervening impossibility is done in following ways-
i. Death or personal incapacity
ii. Destruction of subject-matter
iii. Non - existence or non- occurrence of certain essential things
iv. Change of Law
v. Declaration of war
(iii) Discharge by supervening illegality
If after making the contract, its performance becomes impossible due to alteration
of law or act of any person, it is discharged.
(iv) Cases not covered by subsequent impossibility
i. Partial impossibility
ii. Commercial impossibility
iii. Difficulty of performance
iv. Default of a third party.
v. Strikes, lockouts, etc.
(v) It is also known as frustration under English law.
6. By Breach of contract:
It means failure of a party to perform his obligations.
32