Page 41 - 01. Indian Contract Act, 1872
P. 41
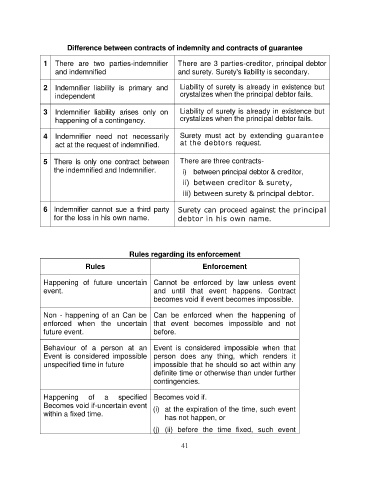
Difference between contracts of indemnity and contracts of guarantee
1 There are two parties-indemnifier There are 3 parties-creditor, principal debtor
and indemnified and surety. Surety's liability is secondary.
2 Indemnifier liability is primary and Liability of surety is already in existence but
independent crystalizes when the principal debtor fails.
3 Indemnifier liability arises only on Liability of surety is already in existence but
happening of a contingency. crystalizes when the principal debtor fails.
4 Indemnifier need not necessarily Surety must act by extending guarantee
act at the request of indemnified. at the debtors request.
5 There is only one contract between There are three contracts-
the indemnified and Indemnifier. i) between principal debtor & creditor,
ii) between creditor & surety,
iii) between surety & principal debtor.
6 Indemnifier cannot sue a third party Surety can proceed against the principal
for the loss in his own name. debtor in his own name.
Rules regarding its enforcement
Rules Enforcement
Happening of future uncertain Cannot be enforced by law unless event
event. and until that event happens. Contract
becomes void if event becomes impossible.
Non - happening of an Can be Can be enforced when the happening of
enforced when the uncertain that event becomes impossible and not
future event. before.
Behaviour of a person at an Event is considered impossible when that
Event is considered impossible person does any thing, which renders it
unspecified time in future impossible that he should so act within any
definite time or otherwise than under further
contingencies.
Happening of a specified Becomes void if.
Becomes void if-uncertain event (i) at the expiration of the time, such event
within a fixed time.
has not happen, or
(j) (ii) before the time fixed, such event
41