Page 64 - Apprentice Manual_Neat
P. 64
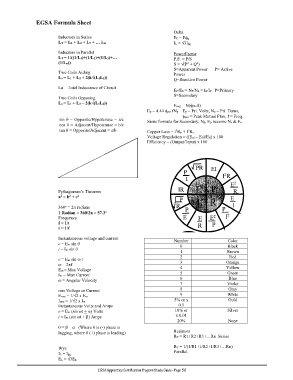
EGSA Formula Sheet
Delta
Inductors in Series EL = Eg
LT = L1 + L2 + L3 + … Ln IL = √3Ig
Inductors in Parallel PowerFactor
LT = 1/((1/L1)+(1/L2)+(1/L3)+… P.F. = P/S
(1/Ln)) S = √(P + Q )
2
2
S=Apparent Power P= Active
Two Coils Aiding Power
La = L1 + L2 + 2(k√(L1L2)) Q=Reactive Power
La = Total Inductance of Circuit
EP/ES = NP/NS = IS/IP P=Primary
S=Secondary
Two Coils Opposing
La = L1 + L2 – 2(k√(L1L2)) Eavg = N(pm/t)
Ep = 4.44pm fNp Ep = Pri. Volts, Np = Pri. Turns,
pm = Peak Mutual Flux, f = Freq.
sin θ = Opposite/Hypotenuse = a/c Same formula for Secondary, Np, Ep become Ns & Es.
cos θ = Adjacent/Hypotenuse = b/c
tan θ = Opposite/Adjacent = a/b Copper Loss = I Rp + I Rs.
2
2
Voltage Regulation = ((Enl – Efl)/Efl) x 100
Efficiency = (Output/Input) x 100
Pythagorean’s Theorem
2
2
2
a = b + c
360 = 2 radians
o
1 Radian = 360/2 = 57.3
o
Frequency
f = 1/t
t = 1/f
Instantaneous voltage and current Number Color
e = Em sin θ 0 Black
i = Im sin θ
1 Brown
2 Red
e = Em sin t
= 2f 3 Orange
Em = Max Voltage 4 Yellow
Im = Max Current 5 Green
= Angular Velocity 6 Blue
7 Violet
rms Voltage or Current 8 Gray
Erms = 1/√2 x Em 9 White
Irms = 1/√2 x Im 5% or x Gold
Instantaneous Volts and Amps 0.1
e = Em (sin t + ) Volts 10% or Silver
i = Im (sin t + ) Amps x 0.01
20% None
θ = – (Where θ is (-) phase is
lagging, where θ (+) phase is leading) Resistors
RT = R1+R2+R3+…Rn Series
Wye RT = 1/(1/R1+1/R2+1/R3+…Rn)
IL = Ig Parallel.
EL = √3E
EGSA Apprentice Certification Program Study Guide - Page 56