Page 209 - The Power of Light, Colour and Sound for Health and Wellness draft
P. 209
4. Near infrared spectroscopy
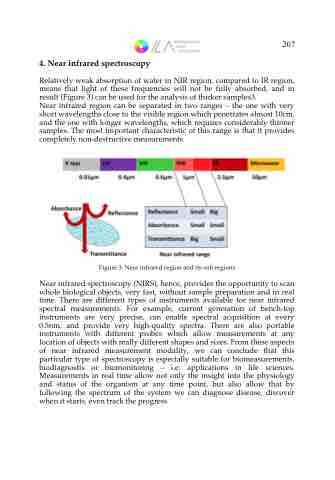
Relatively weak absorption of water in NIR region, compared to IR region, means that light of these frequencies will not be fully absorbed, and in result (Figure 3) can be used for the analysis of thicker samples3.
Near infrared region can be separated in two ranges – the one with very short wavelengths close to the visible region which penetrates almost 10cm, and the one with longer wavelengths, which requires considerably thinner samples. The most important characteristic of this range is that it provides completely non-destructive measurements.
Figure 3. Near infrared region and its sub regions
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), hence, provides the opportunity to scan whole biological objects, very fast, without sample preparation and in real time. There are different types of instruments available for near infrared spectral measurements. For example, current generation of bench-top instruments are very precise, can enable spectral acquisition at every 0.5nm, and provide very high-quality spectra. There are also portable instruments with different probes which allow measurements at any location of objects with really different shapes and sizes. From these aspects of near infrared measurement modality, we can conclude that this particular type of spectroscopy is especially suitable for biomeasurements, biodiagnostis or biomonitoring – i.e. applications in life sciences. Measurements in real time allow not only the insight into the physiology and status of the organism at any time point, but also allow that by following the spectrum of the system we can diagnose disease, discover when it starts, even track the progress.
207