Page 57 - Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as an Emerging Paradigm for Regenerative Therapy and Nano-Medicine
P. 57
Yin et al. Biomarker Research (2019) 7:8 Page 4 of 8
ischaemia reperfusion injury model, injection of bone large amounts of neprilysin, the most prominent en-
marrow-derived MSCs-derived exosomes reduced zyme that degrades β-amyloid peptide in the brain.
apoptosis and myocardial infarct size and subse- Transfer of exosomes into neuroblastoma N2a cells
quently improved heart functions by inducing cardio- led to reductions in both secreted and intracellular
myocyte autophagy via AMPK/mTOR and Akt/mTOR β-amyloid peptidelevels, whichmight beathera-
pathways [47]. peutic approach to Alzheimer’s disease [51]. The re-
sults of migration assay and capillary network
Neurological disease formation assay showed that exosomes secreted by
MSC-Exosomes have shown potential therapeutic adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs-Exos) promoted
benefit in the treatment of neurological and neurode- the mobility and angiogenesis of brain microvascular
generative diseases. One of the most outstanding re- endothelial cells (BMECs) after oxygen-glucose
sults in the field is the fact that systemically injected deprivation (OGD) via miR-181b-5p/TRPM7 axis [52].
exosomes are able to cross the blood-brain barrier Injection of exosomes from mouse bone marrow
(BBB) and achieve the brain parenchyma. Systemic MSCs could rescue cognition and memory impair-
delivery of targeted exosomes containing a siRNA ment according to results of the Morris water maze
against α-synuclein reduced the mRNA and protein test, reduced plaque deposition, and Aβ levels in the
levels of α-synuclein in the brain [48, 49]. Xin et al. brain; could decrease the activation of astrocytes and
also reported that rat bone marrow derived MSCs de- microglia; could down-regulate proinflammatory cyto-
rived EVs enriched with the miR-17-92 cluster en- kines (TNF-α and IL-1β); and could up-regulate
hanced oligodendrogenesis neurogenesis neural anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and -10) in AD
plasticity and functional recovery after stroke possibly mice, as well as reduce the activation of signal trans-
by suppressing PTEN and subsequently by increasing ducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and
the phosphorylation of proteins downstream of PTEN NF-κBinAPP/PS1doubletransgenicmice[53].
including of the protein kinase B/mechanistic target
of rapamycin/glycogen synthase kinase 3β signaling Immune disease Potent immunomodulatory properties
pathway [50]. Katsuda et al. used exosomes secreted of MSCs-exo has been evaluated. Exosomes have been
from human adipose tissue-derived MSCs that contain observed to play crucial roles in carrying and presenting
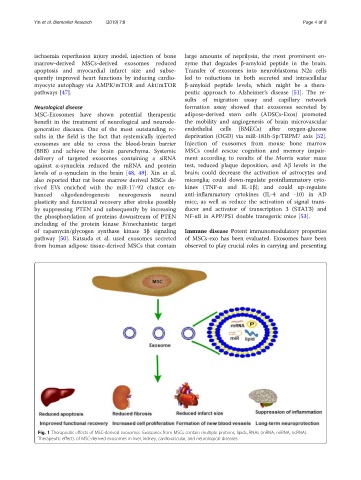
Fig. 1 Therapeutic effects of MSC-derived exosomes. Exosomes from MSCs contain multiple proteins, lipids, RNAs (mRNA, miRNA, ncRNA).
Therapeutic effects of MSC-derived exosomes in liver, kidney, cardiovascular, and neurological diseases