Page 293 - Magistrates Conference 2019
P. 293
10
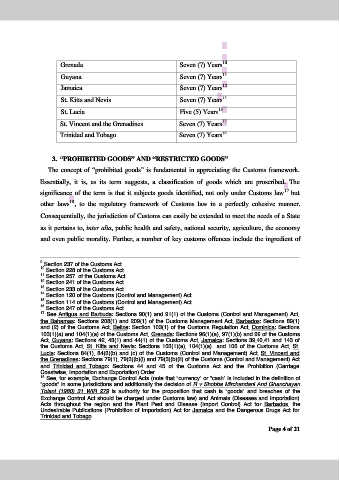
Grenada Seven (7) Years
11
Guyana Seven (7) Years
12
Jamaica Seven (7) Years
13
St. Kitts and Nevis Seven (7) Years
14
St. Lucia Five (5) Years
15
St. Vincent and the Grenadines Seven (7) Years
16
Trinidad and Tobago Seven (7) Years
3. “PROHIBITED GOODS” AND “RESTRICTED GOODS”
The concept of “prohibited goods” is fundamental in appreciating the Customs framework.
Essentially, it is, as its term suggests, a classification of goods which are proscribed. The
17
significance of the term is that it subjects goods identified, not only under Customs law but
18
other laws , to the regulatory framework of Customs law in a perfectly cohesive manner.
Consequentially, the jurisdiction of Customs can easily be extended to meet the needs of a State
as it pertains to, inter alia, public health and safety, national security, agriculture, the economy
and even public morality. Further, a number of key customs offences include the ingredient of
9 Section 237 of the Customs Act
10 Section 228 of the Customs Act
11 Section 257 of the Customs Act
12 Section 241 of the Customs Act
13 Section 233 of the Customs Act
14 Section 120 of the Customs (Control and Management) Act
15 Section 114 of the Customs (Control and Management) Act
16 Section 247 of the Customs Act
17 See Antigua and Barbuda: Sections 90(1) and 91(1) of the Customs (Control and Management) Act,
the Bahamas: Sections 208(1) and 209(1) of the Customs Management Act, Barbados: Sections 89(1)
and (2) of the Customs Act, Belize: Section 103(1) of the Customs Regulation Act, Dominica: Sections
103(1)(a) and 104(1)(a) of the Customs Act, Grenada: Sections 96(1)(a), 97(1)(b) and 99 of the Customs
Act, Guyana: Sections 42, 43(1) and 44(1) of the Customs Act, Jamaica: Sections 39,40,41 and 143 of
the Customs Act, St. Kitts and Nevis: Sections 103(1)(a), 104(1)(a) and 106 of the Customs Act, St.
Lucia: Sections 84(1), 84(3)(b) and (c) of the Customs (Control and Management) Act, St. Vincent and
the Grenadines: Sections 79(1), 79(3)(b)(i) and 79(3)(b)(ii) of the Customs (Control and Management) Act
and Trinidad and Tobago: Sections 44 and 45 of the Customs Act and the Prohibition (Carriage
Coastwise, Importation and Exportation) Order
18 See, for example, Exchange Control Acts (note that “currency” or “cash” is included in the definition of
“goods” in some jurisdictions and additionally the decision of R v Shobba Mirchandani And Ghanchayan
Tolani (1980) 31 WIR 279 is authority for the proposition that cash is “goods” and breaches of the
Exchange Control Act should be charged under Customs law) and Animals (Diseases and Importation)
Acts throughout the region and the Plant Pest and Disease (Import Control) Act for Barbados, the
Undesirable Publications (Prohibition of Importation) Act for Jamaica and the Dangerous Drugs Act for
Trinidad and Tobago
Page 4 of 21